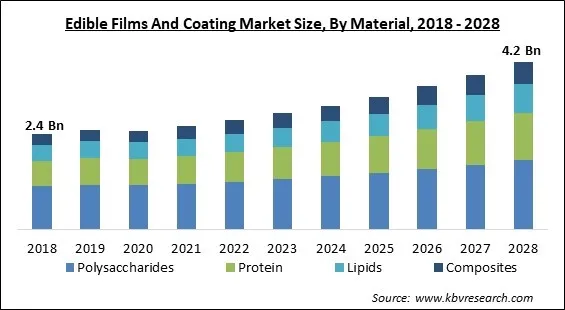
The Global Edible Films And Coating Market size is expected to reach $4.2 billion by 2028, rising at a market growth of 7.5% CAGR during the forecast period.
The edible coating is a green technology that is used to regulate gas exchange, moisture transfer, and oxidation processes in a variety of products. One of the most significant advantages of employing edible films and coatings is that various active chemicals can be included in the polymer matrix and taken with food, improving safety along with nutritional and sensory properties. Manufacturers of food products have strengthened their efforts to extend shelf life and improve existing packaging technologies, ensuring microbial safety and food preservation from the effects of external variables. As a result, new product developments from producers are expected to contribute to the edible films and coatings market's growth.
The edible films and coatings market would be pushed by consumers' greater adaptation of eco-friendly packaging options. This technology can help to improve the product's quality, shelf life, safety, and functionality. Increased use of plastic in food packaging and transport raises concerns because it is hard to decompose properly. Edible films and coatings are one of the finest prospective food packaging alternatives since they can increase food storage, give an alternative to conventional packaging solutions, are biodegradable and eco-friendly, and can extend product shelf life.
Apart from packaging replacements to artificial packaging, the product has a lot of benefits. Polymer is found in edible materials, and it has several advantages, including a low unit of weight and excellent tensile qualities. Natural biopolymers have various advantages in life sciences since they can be obtained from marine life, agriculture, or animals, and they are biocompatible and biodegradable. As a result, manufacturing organizations are actively spending in research and development.
Benefits of edible coating include minimizing packaging waste, extending the shelf life of fresh and minimally processed products, and protecting them from hazardous environmental effects by preserving oxygen, carbon dioxide, moisture, scent, and taste compound transmission in a food system. Edible Coatings, improve shelf life, limit water, and moisture loss, delay ripening, and prevent microbiological growth in fresh fruits and vegetables.
The COVID-19 pandemic has wreaked devastation on economies all around the world. Many industries are affected by pandemics because their economic flow is slowed. The food packaging business, like other industries, harmed their economic growth. Due to the country-by-country lockdown, customers' demand for food, fruits, and vegetables decreased, negatively impacting the edible films and coatings market during the era. Consumer shopping behavior and consumption patterns changed dramatically as a result of the pandemic. Reduced output, lower consumer demand, a gap in the supply chain, as well as import and export restrictions. These factors all impede the expansion of the edible film and coating business; nevertheless, as things return to normal after the COVID era, new market opportunities would emerge, and the edible film and coating market is expected to grow.
Traditional artificial food packaging materials have a number of drawbacks in terms of environmental contamination and the use of non-renewable resources in manufacturing. The search for alternative packaging materials and package formats has risen dramatically. Sustainability, the environment, ethics, food safety, food quality, and product costs are all becoming increasingly relevant aspects for modern-day customers when purchasing food goods, and a number of these topics are regulated by food packaging laws. All of these issues have influenced the food packaging industry's growing demand for edible coatings. Since these edible films are made from natural and organic ingredients, such as wheat gluten, whey protein, maize zein, waxes, cellulose derivatives, and pectins, these edible films are made from fruits, and nuts, grains, and vegetables.
Oxo-biodegradable plastics are manufactured from regular plastics and combined with additives to stimulate biodegradation. The principal result of oxidation, on the other hand, is the fragmentation of the substance or product into small particles that end up in the environment. As a result, some companies are producing edible wrapping to extend the storage life of fruits and vegetables, reducing waste and improving shelf life. Apeel Sciences, a start-up established in the United States, developed an edible existence coating for fruits called Apeel to combat food waste, and plastic packaging waste, and deliver up to two times the shelf-life in the entire food business. Apeel is created from plant skins, peels, and seeds, which include food components.
Despite the obvious benefits of edible coatings, some obstacles prevent edible coatings from being used on a large basis. The use of propolis-based edible coatings in the food sector is restricted due to their intense, distinctive scent and taste. When compared to untreated tomato, candelilla wax loaded with F. cernua active constituents had poorer sensory acceptance. As per Tahir et al., a high concentration of gum edible coating may harm sensory perceptions of coated products. Similarly, Sucheta et al. found that tomatoes covered with composite edible films including commercial pectin, maize flour, and beetroot powder lost their color angle over time as compared to uncoated tomatoes. Stability of bioactive components, poor film-forming characteristics, and surface adhesion may be an additional problem that limits commercial applications of aloe Vera gel edibles, in addition to their negative impact on sensory quality.
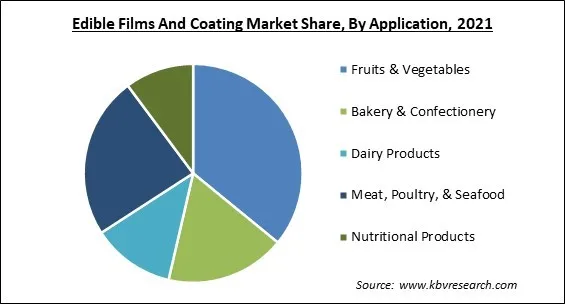
Based on Application, the market is segmented into Fruits & Vegetables, Bakery & Confectionery, Dairy Products, Meat, Poultry, & Seafood, and Nutritional Products. The Meat, Poultry & Seafood segment recorded a substantial revenue share in the edible films and coating market in 2021. The meat, poultry, and seafood sector are on up surge due to the Non-vegetarians as they are increasingly interested in these products, and consumers prefer to purchase edible films over products packaged in synthetic plastic. Meat, poultry, and fish products contain chitosan, starch, carrageenan, gelatin, and other additives.
Based on Material, the market is segmented into Polysaccharides, Protein, Lipids, and Composites. The Polysaccharides segment acquired the highest revenue share in the edible films and coating market in 2021. This is because Polysaccharides are good for fruits and vegetables because they change the interior environment of the product, extending its shelf life. Edible films and coatings are made from starch, cellulose, carrageenan, carboxymethylcellulose, gums, and other ingredients. Films and coatings made of polysaccharides are slightly less impermeable to O2 and CO2.
| Report Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Market size value in 2021 | USD 2.6 Billion |
| Market size forecast in 2028 | USD 4.2 Billion |
| Base Year | 2021 |
| Historical Period | 2018 to 2020 |
| Forecast Period | 2022 to 2028 |
| Revenue Growth Rate | CAGR of 7.5% from 2022 to 2028 |
| Number of Pages | 166 |
| Number of Tables | 290 |
| Report coverage | Market Trends, Revenue Estimation and Forecast, Segmentation Analysis, Regional and Country Breakdown, Companies Strategic Developments, Company Profiling |
| Segments covered | Material, Application, Region |
| Country scope | US, Canada, Mexico, Germany, UK, France, Russia, Spain, Italy, China, Japan, India, South Korea, Singapore, Malaysia, Brazil, Argentina, UAE, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Nigeria |
| Growth Drivers |
|
| Restraints |
|
Based on Regions, the market is segmented into North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, and Latin America, Middle East & Africa. The Asia Pacific segment registered a significant revenue share in the edible films and coating market in 2021. The edible films and coatings market in this region are dominated by China and Japan. Market expansion would be fueled by the existence of global companies, easy product availability, and rising environmental concerns. Xanthan gum is one of the most widely utilized edible coatings in food products in China, resulting in a significant demand for polysaccharide-based films and coatings. However, in the region, research is being performed to uncover additional sources of edible coatings, which is likely to result in product shelf life and freshness being extended.
Free Valuable Insights: Global Edible Films And Coating Market size to reach USD 4.2 Billion by 2028
The market research report covers the analysis of key stake holders of the market. Key companies profiled in the report include Tate & Lyle PLC, Ingredion, Incorporated, DuPont de Nemours, Inc., Koninklijke DSM N.V., Kerry Group PLC, Döhler Gmbh, Cargill Corporation, Glanbia PLC (Watson Inc.), Lactips , and Pace International, LLC (Valent BioSciences LLC.)
By Application
By Material
By Geography
The edible films and coating market size is projected to reach USD 4.2 billion by 2028.
Edible packaging is becoming more popular as a substitute for plastic packaging are increasing are driving the market in coming years, however, edible coatings' limitations growth of the market.
Tate & Lyle PLC, Ingredion, Incorporated, DuPont de Nemours, Inc., Koninklijke DSM N.V., Kerry Group PLC, Döhler Gmbh, Cargill Corporation, Glanbia PLC (Watson Inc.), Lactips , and Pace International, LLC (Valent BioSciences LLC.)
The expected CAGR of the edible films and coating market is 7.5% from 2022 to 2028.
The Fruits & Vegetables segment acquired maximum revenue share in the Global Edible Films And Coating Market by Application in 2021, thereby, achieving a market value of $1.4 billion by 2028.
The North America market dominated the Global Edible Films And Coating Market by Region in 2021, and would continue to be a dominant market till 2028.
Our team of dedicated experts can provide you with attractive expansion opportunities for your business.

