Germany Carbon Dioxide Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report By Application, By Form, By Source (Ethyl Alcohol, Hydrogen, Ethylene Oxide, Substitute Natural Gas, and Others), and Forecast, 2023 - 2030
Published Date : 02-Sep-2024 |
Pages: 64 |
Formats: PDF |
COVID-19 Impact on the Germany Carbon Dioxide Market
The Germany Carbon Dioxide Market size is expected to reach $602.52 Million by 2030, rising at a market growth of 3.3% CAGR during the forecast period. In the year 2022, the market attained a volume of 1,219.17 Kilo Tonnes, experiencing a growth of 1.0% (2019-2022).
The carbon dioxide market in Germany is a crucial segment of the country's economy. Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a colorless and odorless gas produced naturally through various processes such as respiration and combustion. In recent years, the industry for carbon dioxide in Germany has witnessed significant growth, driven by factors such as increasing industrialization, rising demand for beverages, and the implementation of environmental regulations.
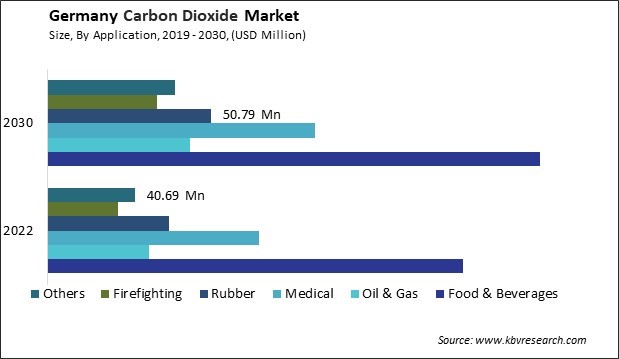
One of the primary drivers of the carbon dioxide market in Germany is the food and beverage industry. Carbon dioxide is widely used to produce carbonated beverages such as soda, beer, and sparkling water. The demand for these beverages has steadily increased, fueled by changing consumer preferences and lifestyle trends. According to Germany Trade & Invest, Germany's food and beverage industry is the fourth-largest sector in the country, contributing a substantial production value of EUR 185.3 billion in 2020. As a result, the beverage industry remains a major consumer of carbon dioxide in Germany, driving the industry's growth.
Furthermore, implementing environmental regulations and initiatives to reduce greenhouse gas emissions has also impacted the carbon dioxide market in Germany. As part of its commitment to combat climate change, Germany has introduced policies to limit carbon emissions and promote using renewable energy sources. This has led to increased investment in technologies for capturing and storing carbon dioxide emissions and the development of alternative sources of carbon dioxide, such as biogas and biomass.
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly impacted the carbon dioxide market in Germany, as it has disrupted supply chains and led to changes in consumer behavior. The lockdown measures implemented to control the spread of the virus resulted in the closure of many businesses and a slowdown in industrial activities, leading to a temporary reduction in the demand for carbon dioxide. Additionally, the decline in tourism and hospitality sectors during the pandemic also affected the demand for carbonated beverages, further impacting the industry.
Market Trends
Growth of the Renewable Energy Sector
The renewable energy sector in Germany has experienced significant growth in recent years. One of the most notable effects of this growth is the reduction in carbon dioxide emissions. Renewable energy sources such as wind, solar, and hydroelectric power produce electricity without emitting carbon dioxide, unlike traditional fossil fuels like coal and natural gas.
According to the International Trade Administration, the country has set ambitious targets to source 80% of its energy from renewables by 2030. By 2022, Germany had made significant progress, achieving 46% of this goal. Renewable sources constituted a substantial 42.3% share of the domestic energy mix. As Germany has increasingly turned to renewables to meet its energy needs, the carbon intensity of its electricity generation has decreased, leading to lower overall carbon dioxide emissions.
Furthermore, the expansion of the renewable energy sector has led to changes in the structure of the carbon dioxide market in Germany. With more renewable energy capacity coming online, there has been increased competition for industry share among different energy sources. As a result, the industry for carbon dioxide emissions allowances has become more dynamic, with prices responding to changes in supply and demand.
Moreover, the growth of renewables has also stimulated innovation and investment in carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies. While renewable energy sources offer a carbon-free alternative to fossil fuels, some sectors of the economy, such as heavy industry and aviation, still rely heavily on carbon-emitting processes. Thus, the growth of the renewable energy sector in Germany has reduced carbon dioxide emissions and transformed the carbon dioxide market while stimulating innovation in carbon capture and storage technologies.
Increasing Emphasis on Reducing Greenhouse
Germany has increasingly emphasized reducing greenhouse gas emissions in the carbon dioxide market in recent years. As one of the leading economies in Europe and a significant contributor to global emissions, Germany's commitment to mitigating climate change is crucial for international efforts to combat environmental degradation. The German government has implemented various policies and initiatives to reduce carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions across different sectors of the economy. One of the central mechanisms for achieving this goal is the establishment of a robust carbon dioxide market.
Germany's carbon dioxide market is part of the broader European Union Emissions Trading System (EU ETS), the largest carbon industry in the world. Germany aims to achieve emission reductions through the EU ETS in industries such as power generation, manufacturing, and aviation. Germany has implemented domestic policies to drive emissions reductions further. The German government has also set ambitious targets for transitioning to renewable energy sources, such as phasing out coal and nuclear power in favor of wind, solar, and other renewables.
Furthermore, Germany promotes international cooperation on climate action through initiatives like the Paris Agreement. By collaborating with other nations, Germany seeks to leverage collective efforts to address the global challenge of climate change. Hence, Germany's concerted efforts in reducing greenhouse gas emissions through robust domestic policies and active participation in international collaborations like the EU ETS.
Competition Analysis
In Germany, the carbon dioxide market is a dynamic sector at the intersection of environmental policy, industrial innovation, and sustainable development. One notable company in Germany's carbon dioxide market is Linde plc. Linde is a global industrial gas and engineering company with a strong carbon capture and utilization presence. Leveraging its expertise in gas separation and purification technologies, Linde develops solutions for capturing CO2 emissions from industrial processes and power plants. The company also explores opportunities for utilizing captured CO2 in applications such as enhanced oil recovery (EOR), carbonation of beverages, and production of synthetic fuels and chemicals.
Another significant player in Germany's carbon dioxide market is BASF SE, a multinational chemical company known for its commitment to sustainability and innovation. BASF is actively involved in research and development initiatives on carbon capture and utilization technologies. The company explores novel approaches for capturing CO2 emissions from industrial sources and developing catalysts and processes for converting CO2 into value-added products such as polymers, plastics, and fertilizers. BASF's efforts in this area align with its broader goal of reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting circular economy principles.
Additionally, Siemens Energy AG is crucial in Germany's carbon dioxide market by focusing on clean energy solutions and decarbonization technologies. Siemens Energy offers a range of products and services related to carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS), including CO2 capture systems, carbon capture plants, and integrated solutions for power generation with carbon capture. The company collaborates with industry partners and research institutions to advance CCUS technologies and support the transition to a low-carbon energy system.
Moreover, ThyssenKrupp AG, a diversified industrial conglomerate, is actively developing carbon capture and utilization technologies. ThyssenKrupp focuses on developing innovative processes for capturing CO2 emissions from steel and cement production, two sectors known for their significant carbon footprint. The company also explores opportunities for utilizing captured CO2 in industrial processes, such as the production of synthetic fuels and chemicals and the mineralization of CO2 for long-term storage.
Furthermore, Evonik Industries AG, a specialty chemicals company, contributes to Germany's carbon dioxide market through its research and development efforts in carbon capture and utilization. Evonik focuses on developing advanced materials and catalysts for CO2 capture and exploring new pathways for converting CO2 into valuable products, including specialty chemicals, polymers, and fuels. Hence, Germany's carbon dioxide market is characterized by diverse companies and organizations committed to advancing carbon capture, utilization, and storage technologies.
List of Key Companies Profiled
- SOL Group
- India Glycols Limited
- Linde PLC
- Taiyo Nippon Sanso Corporation (Mitsubishi Chemical Group Corporation)
- Messer SE & Co. KGaA (Messer Industrie GmbH)
Germany Carbon Dioxide Market Report Segmentation
By Application
- Food & Beverages
- Oil & Gas
- Medical
- Rubber
- Firefighting
- Others
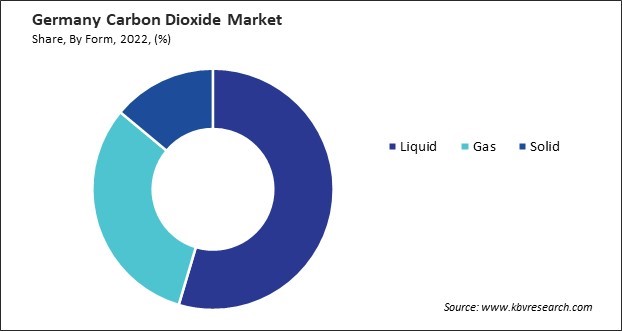
By Form
- Liquid
- Gas
- Solid
By Source
- Ethyl Alcohol
- Hydrogen
- Ethylene Oxide
- Substitute Natural Gas
- Others
1.1 Market Definition
1.2 Objectives
1.3 Market Scope
1.4 Segmentation
1.4.1 Germany Carbon Dioxide Market, by Application
1.4.2 Germany Carbon Dioxide Market, by Form
1.4.3 Germany Carbon Dioxide Market, by Source
1.5 Methodology for the research
Chapter 2. Market Overview
2.1 Introduction
2.1.1 Overview
2.1.1.1 Market Composition and Scenario
2.2 Key Factors Impacting the Market
2.2.1 Market Drivers
2.2.2 Market Opportunities
2.2.3 Market Restraints
2.2.4 Market Challenges
2.2.5 Market Trends
2.3 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
Chapter 3. Strategies Deployed in Carbon Dioxide Market
Chapter 4. Germany Carbon Dioxide Market
4.1 Germany Carbon Dioxide Market by Application
4.2 Germany Carbon Dioxide Market by Form
4.3 Germany Carbon Dioxide Market by Source
Chapter 5. Company Profiles – Global Leaders
5.1 SOL Group
5.1.1 Company Overview
5.1.2 Financial Analysis
5.1.3 Regional Analysis
5.1.4 Recent strategies and developments:
5.1.4.1 Partnerships, Collaborations, and Agreements:
5.1.4.2 Geographical Expansions:
5.1.5 SWOT Analysis
5.2 India Glycols Limited
5.2.1 Company Overview
5.2.2 Financial Analysis
5.2.3 Segmental and Regional Analysis
5.2.4 Research & Development Expenses
5.2.5 SWOT Analysis
5.3 Linde PLC
5.3.1 Company Overview
5.3.2 Financial Analysis
5.3.3 Segmental Analysis
5.3.4 Research & Development Expenses
5.3.5 Recent strategies and developments:
5.3.5.1 Partnerships, Collaborations, and Agreements:
5.3.6 SWOT Analysis
5.4 Taiyo Nippon Sanso Corporation (Mitsubishi Chemical Group Corporation)
5.4.1 Company Overview
5.4.2 Financial Analysis
5.4.3 Segmental Analysis
5.4.4 Research & Development Expenses
5.4.5 SWOT Analysis
5.5 Messer SE & Co. KGaA (Messer Industrie GmbH)
5.5.1 Company Overview
5.5.2 Financial Analysis
5.5.3 Regional Analysis
5.5.4 Recent strategies and developments:
5.5.4.1 Geographical Expansions:
5.5.5 SWOT Analysis
5.6 Acail Gas (Acail Group)
5.6.1 Company Overview
TABLE 2 Germany Carbon Dioxide Market, 2023 - 2030, USD Million
TABLE 3 Germany Carbon Dioxide Market, 2019 - 2022, Kilo Tonnes
TABLE 4 Germany Carbon Dioxide Market, 2023 - 2030, Kilo Tonnes
TABLE 5 Germany Carbon Dioxide Market by Application, 2019 - 2022, USD Million
TABLE 6 Germany Carbon Dioxide Market by Application, 2023 - 2030, USD Million
TABLE 7 Germany Carbon Dioxide Market by Application, 2019 - 2022, Kilo Tonnes
TABLE 8 Germany Carbon Dioxide Market by Application, 2023 - 2030, Kilo Tonnes
TABLE 9 Germany Carbon Dioxide Market by Form, 2019 - 2022, USD Million
TABLE 10 Germany Carbon Dioxide Market by Form, 2023 - 2030, USD Million
TABLE 11 Germany Carbon Dioxide Market by Form, 2019 - 2022, Kilo Tonnes
TABLE 12 Germany Carbon Dioxide Market by Form, 2023 - 2030, Kilo Tonnes
TABLE 13 Germany Carbon Dioxide Market by Source, 2019 - 2022, USD Million
TABLE 14 Germany Carbon Dioxide Market by Source, 2023 - 2030, USD Million
TABLE 15 Germany Carbon Dioxide Market by Source, 2019 - 2022, Kilo Tonnes
TABLE 16 Germany Carbon Dioxide Market by Source, 2023 - 2030, Kilo Tonnes
TABLE 17 Key Information – SOL Group
TABLE 18 Key Information – India Glycols Limited
TABLE 19 Key Information – Linde PLC
TABLE 20 Key Information – Taiyo Nippon Sanso Corporation
TABLE 21 Key Information – Messer SE & Co. KGaA
TABLE 22 Key Information – Acail Gas
List of Figures
FIG 1 Methodology for the research
FIG 2 Germany Carbon Dioxide Market, 2019 - 2030, USD Million
FIG 3 Key Factors Impacting Carbon Dioxide Market
FIG 4 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis - Carbon Dioxide Market
FIG 5 Germany Carbon Dioxide Market share by Application, 2022
FIG 6 Germany Carbon Dioxide Market share by Application, 2030
FIG 7 Germany Carbon Dioxide Market by Application, 2019 - 2030, USD Million
FIG 8 Germany Carbon Dioxide Market share by Form, 2022
FIG 9 Germany Carbon Dioxide Market share by Form, 2030
FIG 10 Germany Carbon Dioxide Market by Form, 2019 - 2030, USD Million
FIG 11 Germany Carbon Dioxide Market share by Source, 2022
FIG 12 Germany Carbon Dioxide Market share by Source, 2030
FIG 13 Germany Carbon Dioxide Market by Source, 2019 - 2030, USD Million
FIG 14 SWOT Analysis: SOL Group
FIG 15 Swot Analysis: India Glycols Limited
FIG 16 SWOT Analysis: Linde plc
FIG 17 SWOT Analysis: Taiyo Nippon Sanso Corporation
FIG 18 SWOT Analysis: Messer SE & Co. KGaA