The Germany Energy ESO Market size is expected to reach $41.2 billion by 2030, rising at a market growth of 16% CAGR during the forecast period.
In Germany's vibrant and dynamic energy ESO market, a comprehensive market overview is essential for understanding the intricate interplay of factors driving innovation, sustainability, and the integration of renewable energy. Germany's ESO sector, a global frontrunner in the energy transition, is distinguished by a convergence of progressive technologies, well-defined regulatory structures, and an unwavering dedication to restructuring the energy domain.
Grid modernization is a key focus in the German energy ESO market, driven by the need for a flexible and intelligent energy infrastructure. Smart grid technologies, including advanced metering systems, grid automation, and real-time monitoring, are pivotal in optimizing grid operations. These technologies enable efficient energy distribution, reduce transmission losses, and support the integration of decentralized energy resources.
As Germany progresses towards its energy transition goals, the energy ESO market landscape will include exploring novel business models. Energy Storage-as-a-Service (ESaaS) and performance-based contracting are gaining traction, providing flexible and cost-effective solutions for businesses and consumers. These models democratize access to advanced energy technologies, aligning with the broader goal of a decentralized and participatory energy system.
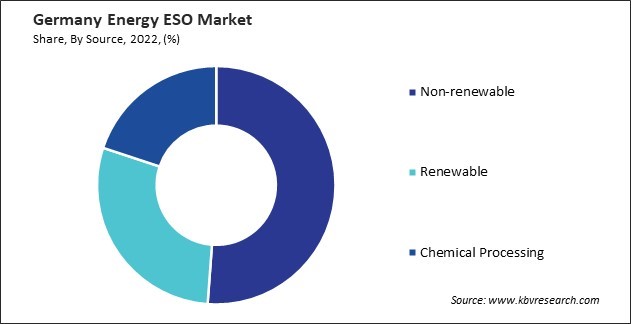
U.S. Energy Information Administration states that Europe's biggest energy consumer is Germany. Primary energy consumption reached 11,769 Petajoules in 2022, with fossil fuels accounting for about 75% of the total, renewable energy accounting for 17.2%, and nuclear energy accounting for 3.2%. The usage of biomass, which makes up over 50% of renewable energy, increased by 1%.
Non-renewable sources are of utmost importance in Germany's energy ESO market as they guarantee a dependable and secure energy provision. Although the nation has made significant strides in transitioning to renewable energy, non-renewable resources such as coal, natural gas, and nuclear power remain essential for meeting base-load demand and maintaining grid stability. Traditional power plants, including fossil fuel-based and nuclear facilities, are integral to the energy infrastructure. These facilities provide a constant and controllable source of electricity, offering a crucial complement to the intermittent nature of renewable energy sources.
The regulatory framework in Germany emphasizes the need for a gradual reduction in dependence on non-renewable sources, aiming to achieve a more sustainable and environmentally friendly energy mix. Striking a balance between the imperatives of energy security, affordability, and environmental responsibility, the German energy ESO market navigates the complexities of integrating non-renewable sources while actively promoting innovations and investments in cleaner, more efficient technologies. Non-renewable energy sources are managed within a comprehensive strategy that acknowledges their role in the energy transition and seeks to minimize their environmental impact over time.
According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, in 2022, 1,449 TWh of natural gas were imported into Germany. The energy mix for 2022 has changed due to the phase-out of nuclear energy and the ongoing development of renewable energies. With a share of 35.3%, mineral oil remained the most significant energy source, followed by natural gas with 23.7%. Natural gas production in the country rose significantly, adding 11.4%. Thus, Germany's energy ESO market strategically incorporates non-renewable sources to ensure stability and meet base-load demand while actively pursuing a gradual transition towards a more sustainable and environmentally friendly energy mix.
In Germany's energy ESO market, cybersecurity and data privacy have emerged as critical considerations amid the increasing reliance on interconnected systems and digital technologies. As the energy sector adopts advanced technologies for grid optimization and data-driven decision-making, ensuring the security and privacy of information has become paramount. One of the primary concerns in the energy ESO sector is the protection of critical infrastructure from cyber threats. A successful cyber-attack on energy storage systems or grid components could disrupt operations, leading to potential power outages and compromising the stability of the energy grid. As a result, there is a growing emphasis on implementing robust cybersecurity measures to safeguard against unauthorized access, data breaches, and malicious activities.
Data privacy is another crucial aspect, especially when analyzing vast amounts of sensitive information for energy optimization. Germany, with its strong data protection regulations, including the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), prioritizes the privacy and rights of individuals. Energy companies operating in the energy ESO market must adhere to these regulations, ensuring consumer data is handled transparently. In alignment with the data protection regulations, energy companies are implementing privacy-by-design principles in developing ESO solutions. Hence, to ensure the reliable and secure operation of the energy grid, energy ESO must invest in robust cybersecurity measures, comply with data privacy regulations, and stay vigilant against evolving cyber threats.
Major telecommunications companies like Deutsche Telekom and Vodafone Germany are prominent players in Germany's energy ESO market. Traditional energy ESO companies like E.ON and RWE are central figures in the German energy landscape and have expanded their focus to include ESO services. These companies are transitioning from conventional energy sources and investing in renewable energy projects, grid modernization, and energy storage solutions. Their expertise in the energy sector allows them to offer comprehensive ESO solutions to businesses and German consumers.
Technology companies and industrial players also contribute significantly to the competitive dynamics of Germany's energy ESO market. Siemens and ABB, for instance, are recognized for their advanced energy management systems, smart grid technologies, and industrial automation solutions. These companies bring technological innovation to the sector, offering integrated solutions for optimizing energy consumption across industries. Energy ESCOs, including MVV Energie and GETEC, provide end-to-end energy solutions, energy efficiency measures, renewable energy integration, and comprehensive ESO services. These companies often collaborate with businesses, municipalities, and industries to implement tailored energy optimization strategies, contributing to the overall competitiveness of Germany's energy ESO market.
Regional and niche players also play a crucial role in the competition landscape. Companies like Innogy and Stromnetz Hamburg operate at the regional level, focusing on specific markets and tailoring their services to meet local needs. These players contribute to the diversity of offerings in Germany's energy ESO market, addressing unique challenges and requirements in different regions.
As Germany modernizes its energy infrastructure, smart grid solution providers, such as Landis+Gyr, are essential contributors to the energy ESO market. These companies provide technologies for grid optimization, demand response, and real-time monitoring. The deployment of smart grid solutions enhances grid reliability and efficiency, contributing to the overall competitiveness of the energy ESO market.
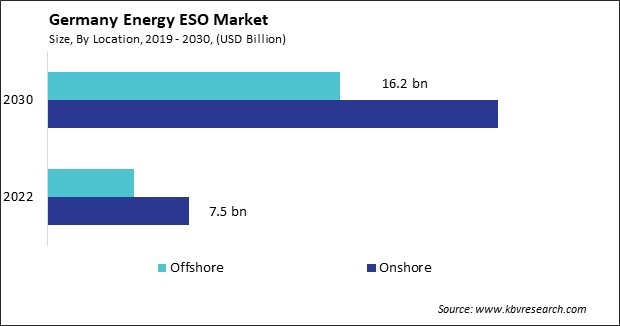
By Location
By Source
By Service
Our team of dedicated experts can provide you with attractive expansion opportunities for your business.

