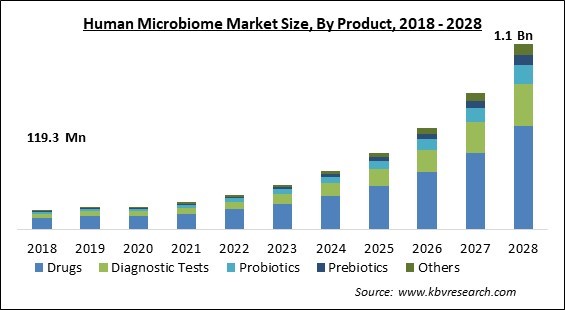
The Global Human Microbiome Market size is expected to reach $1.1 billion by 2028, rising at a market growth of 32.2% CAGR during the forecast period.
The human microbiome is made up of all microbes found on or in human tissues and biofluids, as well as the anatomical places where they live, such as the skin, seminal fluid, mammary glands, uterus, ovarian follicles, saliva, oral mucosa, biliary tract, conjunctiva, and gastrointestinal tract. Bacteria, archaea, fungus, protists, and viruses are all examples of the human microbiota. Despite the fact that micro-animals can survive on humans, they are usually excluded from this description. The term human microbiome is sometimes used in genomics to refer to the aggregate genomes of resident bacteria. Human metagenome, on the other hand, has the same connotation.
Bacteria, viruses, archaea, and eukaryotes live both inside and outside of human bodies, making up the human microbiome. These organisms have an impact on human physiology in both health and disease, enhancing or inhibiting metabolic and immunological systems. Microorganisms colonize diverse areas on and inside the human body, adapting to the unique characteristics of each niche. The gastrointestinal tract is dominated by facultative anaerobes, whereas the nasal cavity, respiratory tract, and skin surface are dominated by strict aerobes. Because of the biological connection of the organisms with the immune system throughout time, the indigenous organisms inside the human body are well adapted to the immune system. Human health and disease etiology are both influenced by changes in the gut microbial flora. These changes are caused by lifestyle choices and the prevalence of an illness. Dysbiosis makes the host more vulnerable to infection, the type of which varies on the anatomical place. The precise metabolic activities and functions of these microorganisms within each bodily location are compensated by the inherent diversity of the human microbiota. As a result, it's critical to comprehend the human microbiome's microbial composition and behaviors as they relate to health and disease.
The COVID-19 pandemic significantly impacted various businesses all over the world. Several developed, developing, and under-developed economies were also demolished due to the advent of the COVID-19 pandemic. In addition, to regulate the rapid diffusion of the infection, governments all over the world enforced stringent lockdown in their countries. The imposition of lockdown across countries resulted in a temporary closure of various companies, businesses, and manufacturing units of several goods and services. Moreover, as a result of government-imposed travel restrictions, the global supply chain was also disrupted. Further, the healthcare sector of all the countries across the world was devastated, which placed a massive burden on researchers and scientists.
The efficiency of medicinal drugs is significantly influenced by the microbiome of the human gut. Several studies have demonstrated that the appropriate balance of microorganisms in the human body can help treat a variety of ailments over time. This link between bacteria and specific diseases may open up new possibilities for drug developers (or vaccine manufacturers). Because microbes are rich in enzymes, they can be exploited in a variety of therapeutic applications, including the search for new medicines. Microbiome therapy has grown in popularity in recent years. The National Institutes of Health (NIH) spent USD 215 million on the Human Microbiome Project (HMP) along with USD 728 million on extramural human microbiome research initiatives outside of the HMP over a ten-year period (fiscal years 2007–2016).
The gut microbiota has been linked to cancer and has been found to boost the efficacy of anticancer drugs. Resistance to chemo medicines or immune checkpoint inhibitors is linked to the altered gut microbiota, whereas supplementation with other bacterial species restores anticancer treatment responses. Altering the gut microbiota can improve the efficacy of anticancer medicines. Regardless of the important findings from preclinical models and clinical data from cancer patients, a better understanding of the microbiota's interactions with cancer therapy can help researchers develop new cancer prevention strategies, stratify patients for more effective treatment, and reduce treatment complications.
Probiotics have not been approved by the FDA as a live biotherapeutic product, which is a biological outcome instead of a vaccine that includes live organisms employed to prevent or cure a disease or condition in humans. However, there are FDA-regulated foods containing probiotics that are legally available, including dietary supplements, and these items cannot be sold to cure, treat, mitigate, or prevent any diseases. Probiotic supplements are heavily promoted in both retail stores and on the internet. Whereas the FDA has not yet approved any probiotics for therapeutic use, some are currently undergoing clinical trials and may soon be sold as biologics or other medications or would be exempted from sellable biological products. The existing FDA regulatory standards for probiotics are not tailored.
Based on Product, the market is segmented into Drugs, Diagnostic Tests, Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Others. In 2021, the drugs segment acquired the largest revenue share of the human microbiome market. The growing number of human microbiome-based therapeutic products in clinical trials, as well as increased funding to develop microbiome-based medications, can be linked to the growth of this segment. Moreover, the increasing efficiency of human microbiome-based drugs is another factor that is propelling the growth of the segment.
Based on Disease Type, the market is segmented into Infectious Diseases, Endocrine & Metabolic Disorders, Gastrointestinal Diseases, Cancer, and Others. In 2021, the gastrointestinal diseases segment recorded a significant reve3nue share of the human microbiome market. The increasing growth of this segment is attributed to the rising prevalence of gastrointestinal diseases. The phrase gastrointestinal disorders refer to any ailment or disease that affects the gastrointestinal tract. The gastrointestinal tract (also known as the GI tract) is a collection of hollow organs that run from the mouth to the stomach.
Based on Technology, the market is segmented into Genomics, Proteomics and Metabolomics. In 2021, the genomics segment procured the highest revenue share of the human microbiome market. A crucial driver for the genomics market is the growing number of initiatives financed by corporate and government entities. With the increasing number of government support initiatives, the growth of this segment is estimated to significantly surge during the forecast period. WGS (whole genome sequencing) is a method for examining complete genomes. Identifying inherited illnesses, defining the mutations that cause cancer progression, as well as tracking disease outbreaks have all benefited from genomic information.
Based on Application, the market is segmented into Therapeutics and Diagnostics. In 2021, the diagnosis segment registered a substantial revenue share of the human microbiome market. The gut microbiota has the potential to be used as a diagnostic biomarker for HCC precancerous conditions, which is propelling the growth of this segment. The gut microbiome also serves as a diagnostic indicator for HCC. The oral microbiota has the potential to be used as a diagnostic biomarker for HCC precancerous conditions.
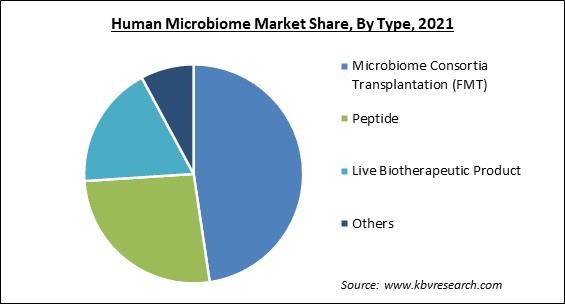
Based on Type, the market is segmented into Microbiome Consortia Transplantation (FMT), Peptide, Live Biotherapeutic Product and Others. In 2021, the microbiome consortia transplantation (FMT) segment recorded the largest revenue share of the human microbiome market. The growth of this segment is attributed to the fact that recurrent Clostridium difficile infection can be successfully treated with FMT. The introduction of a solution of fecal material from a donor into the intestinal tract of a receiver in order to directly affect the recipient's gut microbial composition and bestow a health benefit is known as fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT).
| Report Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Market size value in 2021 | USD 164.4 Million |
| Market size forecast in 2028 | USD 1.1 Billion |
| Base Year | 2021 |
| Historical Period | 2018 to 2020 |
| Forecast Period | 2022 to 2028 |
| Revenue Growth Rate | CAGR of 32.2% from 2022 to 2028 |
| Number of Pages | 296 |
| Number of Tables | 569 |
| Report coverage | Market Trends, Revenue Estimation and Forecast, Segmentation Analysis, Regional and Country Breakdown, Companies Strategic Developments, Company Profiling |
| Segments covered | Product, Disease Type, Technology, Application, Type, Region |
| Country scope | US, Canada, Mexico, Germany, UK, France, Russia, Spain, Italy, China, Japan, India, South Korea, Singapore, Malaysia, Brazil, Argentina, UAE, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Nigeria |
| Growth Drivers |
|
| Restraints |
|
Based on Regions, the market is segmented into North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, and Latin America, Middle East & Africa. In 20212, North America accounted for the largest revenue share of the human microbiome market. The market in North America is being driven by factors such as the rising prevalence of lifestyle illnesses, rising awareness of preventative healthcare, the availability of financing for microbiome research, and the growing number of microbiome research and clinical activities.
Free Valuable Insights: Global Human Microbiome Market size to reach USD 1.1 Billion by 2028
The market research report covers the analysis of key stake holders of the market. Key companies profiled in the report include Seres Therapeutics, Inc., 4D pharma plc, OptiBiotix Health Plc, Synlogic, Inc., Second Genome, Inc., Vedanta Biosciences, Inc., Finch Therapeutics Group, Inc., Ferring Holdings SA, and Enterome.
By Product
By Disease Type
By Technology
By Application
By Type
By Geography
The global human microbiome market size is expected to reach $1.1 billion by 2028.
Application in cancer treatment are increasing are driving the market in coming years, however, stringent government regulations growth of the market.
Seres Therapeutics, Inc., 4D pharma plc, OptiBiotix Health Plc, Synlogic, Inc., Second Genome, Inc., Vedanta Biosciences, Inc., Finch Therapeutics Group, Inc., Ferring Holdings SA, and Enterome.
The Infectious Diseases segment acquired maximum revenue share in the Global Human Microbiome Market by Disease Type in 2021, thereby, achieving a market value of $398.07 Million by 2028.
The North America market dominated the Global Human Microbiome Market by Region in 2021, and would continue to be a dominant market till 2028.
Our team of dedicated experts can provide you with attractive expansion opportunities for your business.

