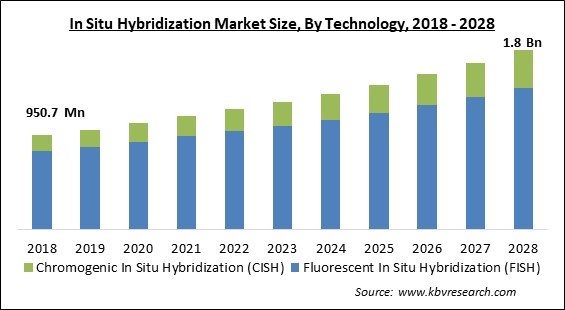
The Global In Situ Hybridization Market size is expected to reach $1.8 billion by 2028, rising at a market growth of 6.9% CAGR during the forecast period.
In situ hybridization (ISH) is a kind of hybridization which locates a particular DNA or RNA sequence in a portion or section of tissue, or when the tissue is small sufficiently, in the whole tissue, in cells, or in circulating tumour cells. It uses a labeled complementary DNA, RNA, or modified nucleic acid strand. Immunohistochemistry, which often localizes proteins in tissue slices, differs from this.
Understanding genes' arrangement, control, and function requires knowing where particular nucleic acid sequences are located on chromosomes or in tissues, which is accomplished using in situ hybridization. Currently, the main methods in use include fluorescent in situ hybridization to identify chromosomal sequences, entire mount in situ hybridization, double identification of RNAs and RNA plus protein, and in situ hybridization to mRNA using oligonucleotide and RNA probes.
One method for figuring out the chromosomal structure is DNA ISH. For instance, fluorescent DNA ISH (FISH) may be employed in medical diagnostic procedures to evaluate chromosomal integrity. A unique nucleic acid sequence may be found and precisely localized inside a single cell using in situ hybridization. Through complementary base pairing, also known as hybridization, with a detectable nucleic acid segment known as a probe, the nucleic acid sequence is selectively bound in a tissue slice.
Three key benefits of in situ hybridization (ISH) are its high sensitivity, exact anatomical localization, and potential for measurement. The nucleic acid cannot be precisely localized inside a tissue using the blotting methods often employed for nucleic acid detection after homogenizing tissues, nucleic acid extraction, and hybridization. Additionally, the blotting techniques could be less sensitive: if just a small number of cells express an adequate quantity of nucleic acid, they would not be picked up by blotting after tissue homogenization but would be by ISH. Nevertheless, ISH is the go-to technique for detecting, localizing, and quantifying nucleic acids, particularly in diverse tissues like the brain.
The COVID-19 pandemic is anticipated to have a significant impact on the market. With the introduction of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, already elevated lab testing requirements became even more global to keep up with enhanced testing criteria to identify probable instances of COVID-19. Thus, there is a considerable increase in the need for clinical diagnostics. The new coronavirus pandemic has created significant disruptions in the healthcare industries all around the globe. A considerable fall in precancer and cancer diagnoses was seen at the pandemic's height because fewer screening tests were conducted. These variables could have recently made in-situ hybridization less effective as a molecular diagnostic tool for cancer. However, the tremendous advancement of FISH probes to detect SARS-CoV-2 RNA in infected cells may have a favorable impact on the sector in the future.
Numerous research on human illnesses conducted over the last several decades has shown recurring genetic aberrations as probable initiating factors for several malignancies. The prevalence of cancer has increased on a global scale. In 2020, cancer will account for over 10 million fatalities, or approximately one in every six fatalities, making it the leading cause of death worldwide. The most common forms of cancer include breast, colon, lung, rectum, and prostate. About one-third of cancer-related deaths are caused by smoking, having a high body mass index, consuming alcohol, consuming less fruits and vegetables, and not exercising.
The increasing quantity and magnitude of investments made in the healthcare industry by governments of different nations are one of the primary drivers of the market's growth. Because of their rapid economic growth and rising healthcare expenses, it is projected that more emerging countries will have more access to high-quality healthcare. This is seen as a sign that the market for in situ hybridization is growing favorably. Due to the increase in health conditions, these countries now have a greater need than ever for different treatments and equipment. Therefore, each of these countries' governments emphasizes increasing the number of payment choices and enhancing citizen access to high-quality healthcare services. During the anticipated period, the market expansion is also fueled by the rising investment in the healthcare sectors.
Many emerging and underdeveloped countries currently have a shortage of qualified professionals who can properly provide therapies. The prevalence of this problem is substantially higher in less developed countries and regions. These nations are anticipated to have a low supply of skilled surgeons and a sizable target patient population base. The molecular details of a chromosome or gene must be understood to perform an ISH-based test. Another obstacle to the industry's expansion is the resistance to switching from manual to automated processes. Thus, the widespread adoption of ISH-based diagnosis is constrained, especially in developing nations, by the need for more competent, trained, and technically aware laboratory staff.
Based on technology, the in situ hybridization market is divided into Chromogenic In Situ Hybridization (CISH) and Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization (FISH). The Fluorescence In-Situ Hybridization (FISH) segment led the in situ hybridization market in 2021. Using complementary fluorescent probes which attach to the chromosomes at certain places, FISH is a kind of ISH. It gives researchers a way to map and see the genetic components of a single cell. This market category dominated the technology-based market in 2022 because of the broad range of applications it offers. For example, in cytogenetics, this method is used to comprehend diverse chromosomal abnormalities and genetic alterations.
Based on the Probe, the in situ hybridization market is divided into the DNA and RNA. The DNA segment accounted for the largest revenue share in the market in 2021. In ISH, a probe made of tagged complementary single-stranded DNA binds to a particular sequence on the target DNA. The quickness with which tests may be run is one of the significant advantages of DNA probes, making this method one of the critical cytogenetic diagnostic techniques. One of the main factors driving the use of DNA probes for therapeutic use is breast cancer.
Based on product, the in situ hybridization market is segmented into instruments, kits & probes, software, and services. The kits and probes market segment accounted for a considerable revenue share in the in situ hybridization industry in 2021. The need for these goods is anticipated to increase as target conditions like cancer become more prevalent. In addition, the prevalence of genetic disorders such as leukaemia, solid tumors, lymphoma, and autism is expected to rise, accelerating the use of the FISH and CISH probe.
Based on application, the in situ hybridization market is divided into cancer, cytogenetics, developmental biology, infectious diseases, and others. The infectious illnesses segment is anticipated to grow at high rate during the forecast period. FISH (Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization), a technique used in infectiology to detect contagious microorganisms, integrates laboratory medicine with molecular genetics technology. While maintaining cell integrity, fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) is used to locate and identify nucleotide sequences in various materials.
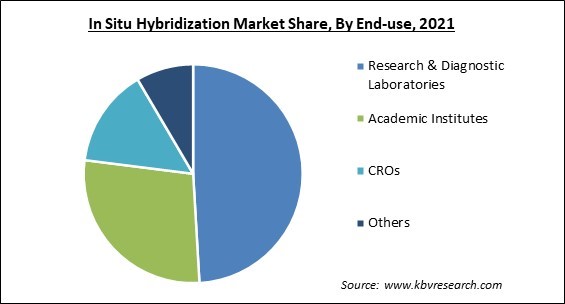
Based on end-use, the in situ hybridization market is segmented into research and diagnostic labs, CROs, academic institutions, and others. The contract research organizations (CROs) showcased the prominent revenue share in the market in 2021. Many organizations contract out their research and clinical trials to CROs, and reasons including a specialized staff, lower costs for businesses, and increased efficiency might motivate enterprises and other organizations to do the same. Therefore, the profitable expansion of this market throughout the anticipated time may be attributable to all of the aforementioned elements.
| Report Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Market size value in 2021 | USD 1.1 Billion |
| Market size forecast in 2028 | USD 1.8 Billion |
| Base Year | 2021 |
| Historical Period | 2018 to 2020 |
| Forecast Period | 2022 to 2028 |
| Revenue Growth Rate | CAGR of 6.9% from 2022 to 2028 |
| Number of Pages | 306 |
| Number of Tables | 550 |
| Report coverage | Market Trends, Revenue Estimation and Forecast, Segmentation Analysis, Regional and Country Breakdown, Companies Strategic Developments, Company Profiling |
| Segments covered | Technology, Application, Product, Probe, End-use, Region |
| Country scope | US, Canada, Mexico, Germany, UK, France, Russia, Spain, Italy, China, Japan, India, South Korea, Singapore, Malaysia, Brazil, Argentina, UAE, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Nigeria |
| Growth Drivers |
|
| Restraints |
|
Based on region, the in situ hybridization market is classified into North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, and LAMEA. The North American region registered the largest revenue share in the market in 2021. This is explained by the widespread use of ISH in R&D in this area. The rising use of ISH, which allows early illness detection, is also a result of the availability of technologically advanced infrastructure. In Situ Hybridization (ISH) market expansion in this area is also anticipated to be fueled by significant companies in the sector and the introduction of cutting-edge products.
Free Valuable Insights: Global In Situ Hybridization Market size to reach USD 1.8 Billion by 2028
The market research report covers the analysis of key stake holders of the market. Key companies profiled in the report include Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., Abbott Laboratories, PerkinElmer, Inc., Agilent Technologies, Inc., Merck Group, Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., Bio-Techne Corporation (Advanced Cell Diagnostics, Inc.), Danaher Corporation (Leica Biosystems), F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., and Neogenomics, Inc.
By Technology
By End Use
By Application
By Product
By Probe
By Geography
The global In Situ Hybridization Market size is expected to reach $1.8 billion by 2028.
Increasing cancer incidence are driving the market in coming years, however, Lack of skilled workers restraints the growth of the market.
Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., Abbott Laboratories, PerkinElmer, Inc., Agilent Technologies, Inc., Merck Group, Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., Bio-Techne Corporation (Advanced Cell Diagnostics, Inc.), Danaher Corporation (Leica Biosystems), F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., and Neogenomics, Inc.
The Research & Diagnostic Laboratories segment acquired maximum revenue share in the Global In Situ Hybridization Market by End-use in 2021 thereby, achieving a market value of $857.3 million by 2028.
The Instruments segment is leading the Global In Situ Hybridization Market by Product in 2021 thereby, achieving a market value of $678.3 million by 2028.
The North America market dominated the Global In Situ Hybridization Market by Region in 2021, and would continue to be a dominant market till 2028; thereby, achieving a market value of $768.5 million by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 6.3 % during the forecast period.
Our team of dedicated experts can provide you with attractive expansion opportunities for your business.

