Int'l : +1(646) 832-2886 | query@kbvresearch.com
Int'l : +1(646) 832-2886 | query@kbvresearch.com
Published Date : 02-Sep-2024 |
Pages: 87 |
Formats: PDF |
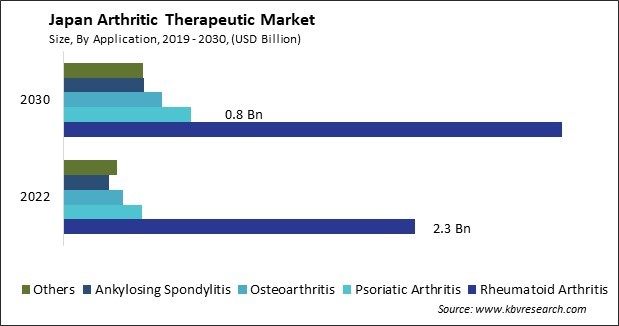
The Japan Arthritic Therapeutic Market size is expected to reach $5.7 Billion by 2030, rising at a market growth of 5.3% CAGR during the forecast period.
The arthritic therapeutic market in Japan represents a significant sector within the country's healthcare landscape, reflecting the prevalence of arthritis and the continuous advancements in treatment options. Arthritis, a chronic condition characterized by inflammation and joint stiffness, affects millions of individuals in Japan, leading to a substantial demand for effective therapies and management strategies. Japan's aging population is a crucial driver of the arthritic therapeutic market, as arthritis becomes more prevalent with age. According to data from the Japanese Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, approximately one in four individuals aged 65 or older in Japan are affected by arthritis, highlighting the significant burden of the disease.
One of the key trends in the Japanese arthritic therapeutic market is the growing adoption of biologic drugs, which target specific molecules involved in the inflammatory process. Biologics have revolutionized the treatment of various forms of arthritis, including rheumatoid arthritis (RA), psoriatic arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis, offering improved efficacy and tolerability compared to traditional therapies. In Japan, biologic agents such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors, interleukin-6 (IL-6) inhibitors, and Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors have gained widespread acceptance and are increasingly prescribed by healthcare providers.
The COVID-19 pandemic has brought unprecedented challenges to the arthritic therapeutic market in Japan. The healthcare system faced disruptions due to lockdowns, restrictions on non-essential medical services, and redirection of resources towards managing the pandemic. As a result, many arthritis patients experience delays in accessing healthcare services, including routine check-ups, medication refills, and physical therapy sessions. Furthermore, the economic repercussions of the pandemic led to financial strain for individuals, impacting their ability to afford arthritic therapeutics and other essential healthcare expenses.
However, the pandemic also prompted innovations in healthcare delivery, such as telemedicine and remote monitoring solutions. According to the International Trade Administration, Japan's telemedicine industry will grow from USD 243 million in 2020 to USD 404.5 million by 2025. The telemedicine industry offered alternative avenues for Japanese patients to consult with healthcare providers and receive necessary care while adhering to social distancing measures.
The pharmaceutical industry in Japan has witnessed significant expansion within the arthritic therapeutic market. One key driver of the expansion within the pharmaceuticals industry in Japan's arthritic therapeutic market is the increasing prevalence of arthritis among the aging population. Japan has one of the most rapidly aging populations globally, with a significant proportion of elderly individuals susceptible to arthritis-related conditions such as osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. According to the Japan Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, the Japanese pharmaceuticals industry in 2021 totaled $106 billion. As a result, pharmaceutical companies have focused on developing innovative therapies tailored to this demographic's specific needs.
Moreover, advancements in medical research and technology have led to the discovery of novel drug targets and treatment approaches for arthritis. Pharmaceutical companies are investing heavily in research and development to bring new and improved medications to the industry. The Japanese government's initiatives to streamline regulatory processes and accelerate drug approvals have also contributed to expanding the pharmaceutical industry in the arthritic therapeutic market.
Furthermore, collaborations between pharmaceutical companies, research institutions, and healthcare providers have fostered an environment conducive to innovation and knowledge sharing within the arthritic therapeutic market. Therefore, Japan's aging population, advancements in medical research, streamlined regulatory processes, and collaborative efforts have propelled significant growth in the pharmaceutical industry's arthritic therapeutic market.
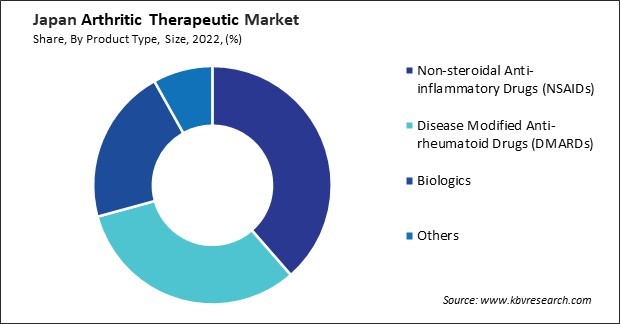
In recent years, Japan has witnessed a notable surge in the popularity of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) within the arthritic therapeutic market. One key factor driving the increasing popularity of NSAIDs in Japan is their effectiveness in relieving arthritic symptoms such as pain, inflammation, and stiffness. NSAIDs work by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins, chemicals in the body that contribute to inflammation and pain.
Furthermore, Japan's aging population has played a significant role in driving the demand for NSAIDs in the arthritic therapeutic market. According to the International Trade Administration, the proportion of the population older than 65 will rise from 29% to 40 % by 2060. With a substantial proportion of the population experiencing age-related joint pain and arthritis, there is a growing need for effective pain management strategies. NSAIDs offer a convenient and accessible option for addressing these symptoms, allowing older adults to maintain an active lifestyle and manage their condition effectively.
Moreover, a diverse range of NSAID formulations in Japan has contributed to their widespread adoption. Patients can choose from various dosage forms, including oral tablets, capsules, topical gels, and patches, allowing personalized treatment approaches based on individual preferences and needs. Hence, the surging popularity of NSAIDs in Japan's arthritic therapeutic market is fueled by their effectiveness, the aging population's increasing demand for pain management solutions, and the diverse range of available formulations catering to individual preferences and needs.
In Japan, the arthritic therapeutic market is a significant sector within the pharmaceutical and healthcare industry. One of the key players in the Japanese arthritic therapeutic market is Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited. Takeda has a strong presence in rheumatology and offers several medications for the treatment of arthritis, including Actemra (tocilizumab), a monoclonal antibody targeting interleukin-6 (IL-6) receptors. Actemra is indicated for rheumatoid arthritis and systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis, providing patients with a biological option to manage inflammation and joint damage. Takeda's commitment to research and development ensures ongoing innovation in arthritic therapeutics.
Eisai Co., Ltd. is also active in the Japanese arthritic therapeutic market, with medications such as Aricept (donepezil) and Fycompa (perampanel) in its portfolio. While these drugs are primarily indicated for Alzheimer's disease and epilepsy, respectively, Eisai is involved in research and development efforts aimed at identifying potential treatments for arthritis and other inflammatory disorders. The company's multidisciplinary approach to drug discovery holds promise for the development of novel therapies in the future.
Another major contributor to the Japanese arthritic therapeutic market is Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation. Mitsubishi Tanabe manufactures Adalat (nifedipine), a calcium channel blocker used in the treatment of hypertension, which is often a comorbidity of arthritis. Additionally, the company produces biologic medications such as Remicade (infliximab) and Simponi (golimumab), TNF inhibitors indicated for rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory conditions. Mitsubishi Tanabe's diverse product portfolio addresses various aspects of arthritis management, catering to the specific needs of patients.
Daiichi Sankyo Company, Limited is another notable player in the Japanese arthritic therapeutic market. Daiichi Sankyo manufactures Loxonin (loxoprofen), a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) commonly prescribed for managing pain associated with arthritis and other musculoskeletal conditions. Additionally, the company is involved in developing biological therapies targeting specific inflammatory pathways implicated in arthritis pathogenesis. Daiichi Sankyo's commitment to innovation underscores its role in addressing the unmet needs of patients with arthritis in Japan.
Further, Astellas Pharma Inc. is actively engaged in the Japanese arthritic therapeutic market by developing and producing medications such as Prograf (tacrolimus) and Advagraf (extended-release tacrolimus). While these drugs are primarily indicated for the prevention of organ rejection in transplant recipients, tacrolimus has shown potential as an adjunct therapy for certain forms of arthritis, particularly in cases where conventional treatments have been ineffective. Astellas' exploration of tacrolimus' immunomodulatory effects highlights the company's commitment to advancing arthritis research and treatment. The competitive landscape of the Japanese arthritic therapeutic market is characterized by ongoing innovation and collaboration aimed at addressing the diverse needs of patients with arthritis and improving their overall quality of life.
By Application
By Product Type