Int'l : +1(646) 600-5072 | query@kbvresearch.com
Int'l : +1(646) 600-5072 | query@kbvresearch.com
Published Date : 15-May-2024 |
Pages: 94 |
Formats: PDF |
The Japan Artificial Intelligence In Banking Market size is expected to reach $7.4 Billion by 2030, rising at a market growth of 31.3% CAGR during the forecast period.
In Japan, the BFSI sector is witnessing a transformative shift driven by the growing recognition of the necessity of artificial intelligence (AI) technologies. As a cornerstone of the Japanese economy and a global financial hub, the BFSI sector faces unique challenges that demand innovative solutions. The integration of AI in Japan's BFSI sector is necessary to address these challenges and unlock new opportunities for growth, efficiency, and customer satisfaction.
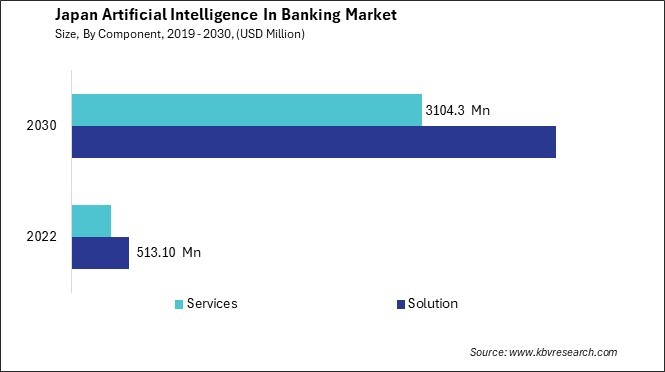
One of the key drivers for adopting AI in the Japanese BFSI sector is the quest for operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Japanese financial institutions are pressured to streamline operations, reduce costs, and improve productivity. AI technologies, such as machine learning and robotic process automation, offer the potential to automate repetitive tasks, optimize workflows, and enhance overall operational efficiency. By leveraging AI, Japanese banks can free up resources to focus on more strategic initiatives while improving their bottom line.
Moreover, the demand for AI in the Japanese BFSI sector is fueled by the need to enhance customer experiences. In an era where digitalization reshapes consumer expectations, Japanese banks are turning to AI to deliver personalized and seamless customer experiences. AI-powered chatbots, virtual assistants, and predictive analytics enable banks to better understand customer needs, provide proactive support, and offer tailored financial products and services. This customer-centric approach is essential for Japanese banks to stay competitive and maintain customer loyalty in a rapidly evolving market.
Furthermore, Japan's BFSI sector recognizes the strategic importance of AI in maintaining global competitiveness. Japanese banks leverage AI to differentiate themselves through innovative products and services as international competition intensifies. AI enables Japanese banks to harness the power of data and analytics to gain insights, identify market trends, and develop strategies that resonate with customers domestically and internationally. By embracing AI, Japanese financial institutions can position themselves as leaders in the global BFSI landscape, driving growth and innovation in the sector.
The Japanese banking sector has recently witnessed an increasing adoption of machine learning (ML) and deep learning technologies to drive innovation, improve operational efficiency, and enhance customer experiences. These advanced AI techniques are being leveraged across various areas within the banking sector, including risk management, fraud detection, customer service, and product development.
Japanese banks are using these technologies to analyze large volumes of data and identify patterns that can help more accurately assess credit, market, and operational risks. By leveraging ML and deep learning algorithms, banks can improve the accuracy of risk models and make better-informed decisions, ultimately strengthening their risk management practices. For example, Mizuho Financial Group, one of Japan's largest financial institutions, has implemented AI-powered risk management systems based on machine learning algorithms.
Another area of application is in fraud detection and prevention. ML and deep learning algorithms can analyze transactional data in real-time to detect suspicious patterns and anomalies that may indicate fraudulent activity. Japanese banks increasingly use these technologies to enhance their fraud detection capabilities, thereby reducing financial losses and protecting customers from fraud-related risks. For example, Mitsubishi UFJ Financial Group (MUFG), another major player in the Japanese banking sector, has integrated machine learning and deep learning algorithms into its fraud detection systems.
Furthermore, ML and deep learning personalize customer experiences in the Japanese banking sector. By analyzing customer data and behavior, banks can use these technologies to offer personalized product recommendations, targeted marketing campaigns, and customized financial advice. This level of personalization can help banks improve customer satisfaction and loyalty in a highly competitive market. Several Japanese banks have deployed AI-powered chatbots for customer service powered by machine learning and natural language processing (NLP) algorithms. Thus, as these technologies continue to advance, their adoption is expected to further accelerate, leading to continued innovation and transformation in the Japanese banking sector.
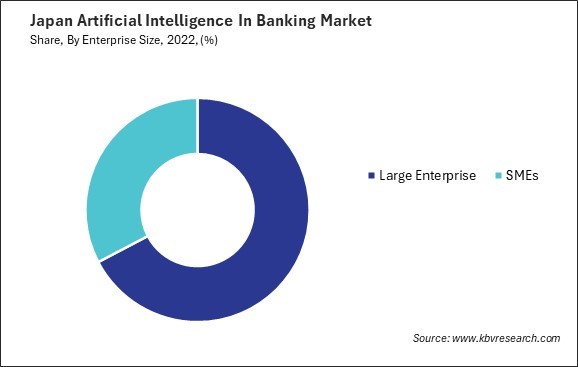
The rise of BFSI SMEs can be attributed to several factors, including regulatory changes that have encouraged entrepreneurship, advancements in technology that have lowered barriers to entry, and an increasing demand for specialized financial services tailored to the needs of specific industries and customer segments. One significant trend in the growth of BFSI SMEs in Japan is the emergence of fintech startups leveraging technology to disrupt traditional financial services. These startups are often agile and innovative, offering new solutions in digital banking, payment processing, lending, and insurance. Their agility and focus on customer-centric solutions have enabled them to carve out niches in the market and compete with established players.
Additionally, Japan's government has been actively promoting entrepreneurship and innovation in the financial sector, creating a conducive environment for the growth of BFSI SMEs. Initiatives such as regulatory sandboxes and funding programs for fintech startups have provided support and incentives for entrepreneurs to launch new ventures in the BFSI space. This has led to a diversification of the financial services landscape in Japan, with BFSI SMEs bringing new ideas and products to market.
The support and encouragement provided by the Japanese government through regulatory sandboxes and funding programs have created an environment conducive to innovation in the BFSI sector. This has enabled fintech startups, including those focusing on AI in banking, to thrive and expand their operations, further driving the demand for AI technologies. As these startups disrupt traditional financial services with innovative digital solutions, they are driving the adoption of AI in banking. Their focus on leveraging AI for areas such as digital banking, payment processing, lending, and insurance has increased demand for AI-powered solutions. Hence, these factors are expected to support the growth of the artificial intelligence in banking market throughout the forecast period.
In Japan, the artificial intelligence in banking market is witnessing several companies leading the way in providing AI-powered solutions tailored for the banking industry. These companies offer diverse AI applications, including machine learning algorithms, natural language processing (NLP), robotic process automation (RPA), and predictive analytics, aimed at enhancing various aspects of banking operations, customer experiences, risk management, and more.
One prominent Japanese artificial intelligence in banking market player is NEC Corporation, a global leader in integrating IT and network technologies. NEC provides AI solutions for banking institutions focusing on fraud detection, customer service automation, and operational efficiency. NEC's AI technologies are designed to analyze large volumes of data to deliver actionable insights and improve decision-making processes for banks.
Another key player in the Japanese artificial intelligence in banking market is Fujitsu Limited, a leading provider of IT products and services. The company offers AI solutions that enable banks to automate processes, enhance customer experiences, and optimize operations. Fujitsu's AI technologies leverage advanced analytics and machine learning to deliver personalized services and improve the overall efficiency of banking operations.
IBM Japan is also a significant player in the Japanese artificial intelligence in banking market, leveraging its global AI and cognitive computing expertise. IBM provides AI-powered solutions for risk management, customer engagement, and operational excellence in banking. IBM's AI technologies, including its Watson platform, enable banks to harness the power of data and AI to drive innovation and improve business outcomes.
In addition to these global players, a growing number of domestic startups and technology firms in Japan specialize in AI solutions for banking. These companies focus on niche areas such as chatbots for customer service, AI-powered analytics for risk management, and AI-driven personalization for customer experiences. Their innovative approaches and agile development methodologies make them key contributors to the evolving landscape of AI in Japanese banking.
Overall, the presence of these companies in the Japanese artificial intelligence in banking market reflects the growing importance of AI technologies in the country's banking sector. As AI continues transforming banking operations and customer interactions, these companies are at the forefront of driving innovation and shaping Japan's banking future.
By Component
By Enterprise Size
By Technology
By Application