Int'l : +1(646) 600-5072 | query@kbvresearch.com
Int'l : +1(646) 600-5072 | query@kbvresearch.com
Published Date : 15-Feb-2024 |
Pages: 70 |
Formats: PDF |
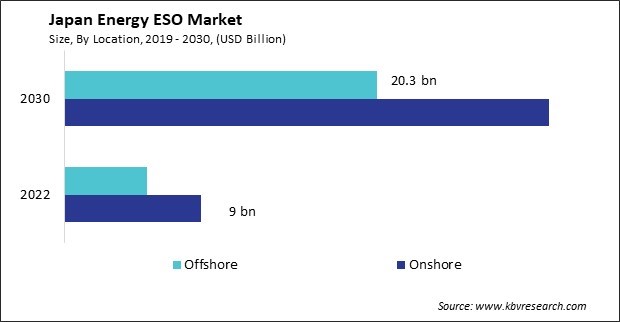
The Japan Energy ESO Market size is expected to reach $51.6 billion by 2030, rising at a market growth of 17.6% CAGR during the forecast period.
Japan's energy ESO market presents a dynamic and evolving landscape driven by the nation's commitment to sustainability, resilience, and innovation in its energy sector. The industry's overarching focus is optimizing energy ESO systems to address the challenges posed by integrating renewable energy ESO, grid modernization efforts, and the need for a reliable, adaptive energy infrastructure.
Japan's geographical constraints, characterized by limited land availability and susceptibility to natural disasters, have spurred unique developments in the energy ESO market. Resilience against natural disasters is a critical aspect influencing the energy ESO market in Japan. With a history of earthquakes and typhoons, the nation prioritizes the development of energy infrastructure capable of withstanding disruptions. Energy ESO becomes integral in enhancing the resilience of the energy grid, allowing for rapid response and recovery in the aftermath of unforeseen.
Microgrid development is gaining prominence in Japan, particularly in rural and remote areas. Energy ESO is pivotal in these microgrid systems, offering localized energy generation, storage, and distribution solutions. The flexibility and resilience provided by energy ESO contribute to the sustainability and reliability of microgrids, aligning with Japan's broader goals of creating decentralized and resilient energy systems.
In recent years, Japan has witnessed a remarkable surge in the integration of renewable energy sources, propelling the energy ESO market to new heights. This trend reflects a paradigm change in the country's energy landscape, driven by innovative technologies, regulatory incentives, and a growing commitment to sustainable practices. Floating solar farms represent a unique facet of Japan's renewable energy strategy. With limited land availability, the country has embraced installing solar panels on water bodies. This innovative approach addresses land scarcity and presents a novel challenge for optimizing energy storage. The variable output from these floating solar installations necessitates sophisticated energy storage optimization to maintain grid stability and reliability.
Community-based renewable energy initiatives have also gained significant traction in Japan, further propelling the integration of renewables into the energy landscape. These projects involve active engagement from local communities in renewable energy generation, fostering a sense of ownership and sustainability. Energy ESO becomes a linchpin in supporting the decentralization of energy systems in Japan, equipping these community-based initiatives with the tools needed to manage fluctuations in energy generation and consumption effectively. Therefore, Japan's energy ESO market is undergoing a transformative shift with a surge in renewable energy integration.
Japan's energy ESO market has witnessed a significant transformation driven by digitization trends. One notable focus is on the development of smart grids and digital infrastructure. Through the integration of advanced sensors, communication networks, and data analytics, Japan aims to optimize energy distribution, improve reliability, and accommodate the increasing share of renewable energy sources.
Japan's energy ESO market digitization initiative is characterized by the strategic implementation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices and cutting-edge sensors. The Japanese imperative for meticulous energy management is at the forefront of this movement. The precision afforded by real-time monitoring and data analytics, facilitated by advanced sensors and IoT devices, aligns seamlessly with Japan's commitment to optimizing energy consumption. This translates to economic savings and resonates with the nation's meticulous approach to resource conservation and sustainable practices.
Japan's commitment to increasing the use of electric vehicles (EVs) also contributes to the digitization efforts in the energy ESO market. Smart charging infrastructure and grid management systems are being developed to accommodate the growing number of EVs, reflecting a broader trend towards embracing digital solutions for a more sustainable and integrated energy ecosystem. Thus, Japan's energy ESO market is undergoing a transformative shift driven by digitization, particularly in the development of smart grids and IoT-driven energy management.
According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, clean energy vehicles, or CEVs, are used in Japan to distinguish environmentally friendly automobiles from those that run on fossil fuels. Battery electric vehicles (BEVs), plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs), and fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) are among the CEVs that the Government of Japan (GOJ) is offering to fund partially. In 2021, a car can receive up to 800,000 Japanese Yen, or roughly 7,200 US dollars, in CEV subsidies. This, in turn, will result in increased ownership of electric vehicles, necessitating the need for charging infrastructure. Thus, Japan's energy ESO market is undergoing a transformative shift driven by digitization.
Japan's energy ESO market is witnessing intense competition, fueled by the nation's commitment to renewable energy integration and grid modernization. As a major player in the global energy landscape, Japan's unique challenges and strategic initiatives have created a dynamic and competitive industry environment characterized by innovation, collaboration, and technological advancements.
Established energy storage solution providers, domestic and international, are at the forefront of competition, seeking to capitalize on Japan's evolving energy landscape. Leading Japanese companies such as NEC Corporation, Panasonic Corporation, and Toshiba Energy Systems & Solutions Corporation have actively developed and deployed advanced energy ESO technologies. These industry incumbents leverage their expertise in battery technology, grid management systems, and longstanding partnerships to maintain a competitive edge.
International players have also entered the fray, bringing global experience and diverse technological portfolios to the Japanese energy ESO market. Companies like Siemens Energy, ABB, and Samsung SDI strategically position themselves to capture an industry share by offering innovative solutions that align with Japan's specific energy needs and regulatory frameworks. The competition is not only centered on the technological prowess of these companies but also on their ability to adapt to local nuances and collaborate effectively with Japanese stakeholders.
Several local companies in Japan contribute significantly to the energy ESO market. Prominent utilities such as Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings (TEPCO) and Chubu Electric Power are actively involved in generating, transmitting, and distributing electricity. These companies prioritize digitalization and smart grid initiatives. JERA, a joint venture between TEPCO and Chubu Electric, plays a pivotal role in power generation, emphasizing both traditional and renewable sources. SoftBank Energy specializes in renewable energy projects, contributing to Japan's sustainable energy goals. Technology giants like NEC Corporation and Mitsubishi Electric Corporation provide innovative solutions in smart energy management systems and IoT technologies, driving the digitization of Japan's energy sector.
By Location
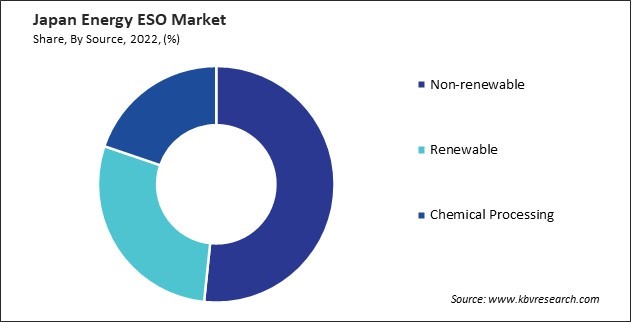
By Source
By Service