Japan Rabies Vaccine Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report By Prophylaxis Type (Post-exposure Prophylaxis, and Pre-exposure prophylaxis), By End User, By Application (Human, and Animal), By Product Type, and Forecast, 2023 - 2030
Published Date : 28-Oct-2024 |
Pages: 75 |
Report Format: PDF + Excel |
COVID-19 Impact on the Japan Rabies Vaccine Market
The Japan Rabies Vaccine Market size is expected to reach $78.44 Million by 2030, rising at a market growth of 4.3% CAGR during the forecast period.
The rabies vaccine market in Japan has witnessed steady growth over the years. Japan has a relatively low incidence of rabies compared to other countries, but the risk of the disease persists, especially with globalization and international travel. In Japan, rabies cases are sporadic, with occasional outbreaks among wild animals such as raccoons and bats. Despite the low incidence, the Japanese government maintains stringent control measures to prevent the spread of rabies, including mandatory vaccination of pets and wildlife surveillance programs.
Moreover, the demand for rabies vaccines in Japan is primarily driven by the pet population, which has steadily increased in recent years. According to the Japan Pet Food Association, the number of registered dogs and cats in Japan reached over 22 million in 2020, reflecting a growing trend of pet ownership among Japanese households. As pet owners become more aware of the importance of rabies vaccination in protecting their pets and preventing the spread of the disease, the demand for rabies vaccines is expected to continue growing.
Furthermore, government initiatives aimed at promoting rabies vaccination have contributed to the expansion of the rabies vaccine market. The Japanese Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW) recommends routine vaccination of pets against rabies and provides subsidies to local governments to support vaccination programs. These efforts have helped increase public awareness and accessibility to rabies vaccines across Japan.
The outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic in Japan has had a significant impact on healthcare systems including the rabies vaccine market. The focus on controlling the spread of COVID-19 has led to disruptions in routine healthcare services and vaccination programs. While efforts to combat COVID-19 remain a priority, it is essential to ensure the continuity of essential vaccination services, including those for rabies, to prevent outbreaks of vaccine-preventable diseases.
Market Trends
Increasing trend of international travel
In recent years, Japan has witnessed a significant surge in international travel. The heightened travel activity has raised concerns regarding the potential exposure to infectious diseases, including rabies, which remains a significant public health issue in Japan. According to the International Trade Administration, before the COVID-19 pandemic, Japan was the second-largest contributor of overseas travelers, with an annual influx of 3.8 million visitors. This robust tourism significantly bolstered the economy, generating $13 billion in spending. With travelers venturing into regions where rabies is endemic or prevalent, the demand for pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) through vaccination has surged.
The increasing international travel trend has led to a parallel rise in Japan's demand for rabies vaccines. Travelers seeking protection against rabies often opt for vaccination as a preventive measure, especially if their itineraries include destinations with known rabies risks. Moreover, the Japanese government's emphasis on promoting health and safety during travel has further fueled awareness about the importance of rabies vaccination among outbound travelers.
Additionally, healthcare providers have been actively promoting rabies vaccination as part of travel health consultations, emphasizing the necessity of adequate preparation against potential health risks abroad. Thus, the surge in international travel in Japan has led to increased demand for rabies vaccines, prompting proactive measures by travelers and healthcare providers to prioritize protection against infectious diseases.
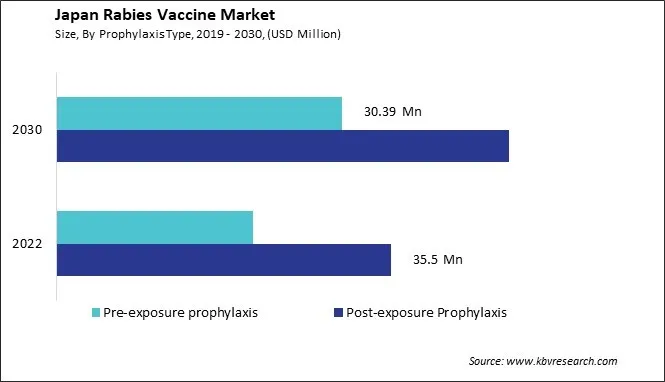
Rising adoption of pre-exposure prophylaxis
Pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) with the rabies vaccine has gained traction in Japan as a preventive measure against this deadly viral disease. The Japanese rabies vaccine market has seen significant developments recently, with a growing emphasis on proactive measures to safeguard public health. PrEP, in particular, has emerged as a key strategy in reducing the risk of rabies transmission, especially in high-risk occupational groups such as veterinarians, animal handlers, and laboratory workers. One of the primary drivers behind the adoption of PrEP in Japan is the country's proactive approach to disease prevention and control.
The pharmaceutical industry in Japan has responded to this growing demand by developing and commercializing rabies vaccines specifically tailored for PrEP. These vaccines are formulated to provide long-lasting immunity with minimal side effects, ensuring compliance and effectiveness among recipients. According to the Japan Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare’s (“MHLW’s”), the Japanese pharmaceuticals industry in 2021 totaled $106 billion. Additionally, advancements in vaccine delivery systems have made PrEP more convenient and accessible, further driving its adoption.
Moreover, Japan's stringent regulations and high standards for healthcare products have contributed to the reliability and efficacy of rabies vaccines available in the industry. As a result, there has been increasing acceptance and uptake of PrEP among individuals in high-risk occupations and travelers to rabies-endemic regions. Furthermore, public awareness campaigns and educational initiatives have played a crucial role in promoting the benefits of PrEP and encouraging its uptake among target populations. Hence, in Japan, the proactive adoption of PrEP with tailored rabies vaccines reflects a commitment to public health supported by advancements in vaccine development, delivery, and regulatory standards.
Competition Analysis
The rabies vaccine market in Japan is crucial for preventing the spread of rabies, a viral disease that poses significant health risks to humans and animals. While Japan has successfully maintained a rabies-free status in domestic animals for many years, the threat of imported cases remains, necessitating the availability of effective vaccines and robust vaccination programs. One of the key players in the Japanese rabies vaccine market is Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited, a leading global biopharmaceutical company with a strong presence in vaccine development and production. Takeda's rabies vaccines are designed to provide reliable protection against the rabies virus, meeting the stringent regulatory requirements set forth by Japanese authorities.
Riken Meijo Co., Ltd. is another notable participant in the Japanese rabies vaccine market. The company specializes in the research, development, and manufacturing of biopharmaceutical products, including vaccines. The company's rabies vaccines are manufactured using advanced biotechnological methods to ensure consistent quality and efficacy. Riken Meijo's commitment to innovation and continuous improvement drives the development of next-generation rabies vaccines, enhancing their effectiveness and safety profiles.
Another significant contributor to the Japanese rabies vaccine market is Kaketsuken, also known as the Chemo-Sero-Therapeutic Research Institute. Kaketsuken is a non-profit organization dedicated to developing and producing vaccines and sera for the prevention and treatment of infectious diseases. The institute's rabies vaccines play a vital role in Japan's public health infrastructure, ensuring the availability of safe and effective vaccines for both humans and animals. Kaketsuken's expertise in vaccine production contributes to the country's preparedness for potential rabies outbreaks.
Kyowa Kirin Co., Ltd. is a pharmaceutical company that also plays a role in the Japanese rabies vaccine market. While not exclusively focused on vaccine production, Kyowa Kirin has diversified operations that include vaccine development and manufacturing. The company's contributions to the rabies vaccine market support Japan's public health objectives by providing additional rabies prevention and control options.
Other companies, such as Daiichi Sankyo Company, Limited, and Astellas Pharma Inc., also plays a role in the Japanese rabies vaccine market, although their primary focus lies in other areas of pharmaceuticals. These companies contribute to the overall healthcare landscape in Japan and play supporting roles in vaccine research, development, or distribution. Hence, the Japanese rabies vaccine market benefits from the contributions of various stakeholders, including pharmaceutical companies, research institutes, and government agencies.
List of Key Companies Profiled
- Cadila Pharmaceuticals Limited
- Bharat Biotech Ltd.
- Serum Institute of India Pvt. Ltd. (Cyrus Poonawalla Group)
- Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH
- Elanco Animal Health, Inc.
- Zoetis, Inc.
- Merck & Co., Inc.
- Novartis AG
- Sanofi S.A.
- Virbac
Japan Rabies Vaccine Market Report Segmentation
By Prophylaxis Type
- Post-exposure Prophylaxis
- Pre-exposure prophylaxis
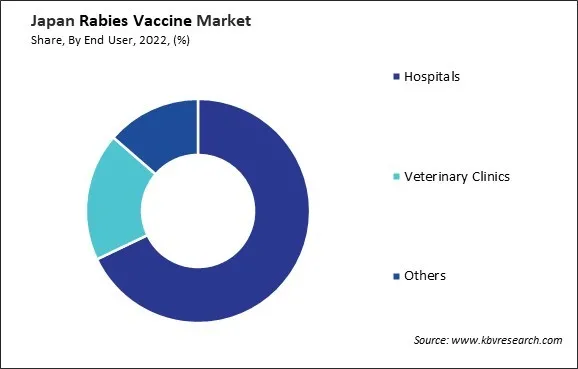
By End User
- Hospitals
- Veterinary Clinics
- Others
By Application
- Human
- Animal
By Product Type
- Chick Embryo Cells Rabies Vaccine
- Human Diploid Cell Vaccine
- Vero cell rabies vaccine
- Others
1.1 Market Definition
1.2 Objectives
1.3 Market Scope
1.4 Segmentation
1.4.1 Japan Rabies Vaccine Market, by Prophylaxis Type
1.4.2 Japan Rabies Vaccine Market, by End User
1.4.3 Japan Rabies Vaccine Market, by Application
1.4.4 Japan Rabies Vaccine Market, by Product Type
1.5 Methodology for the research
Chapter 2. Market Overview
2.1 Introduction
2.1.1 Overview
2.1.1.1 Market Composition and Scenario
2.2 Key Factors Impacting the Market
2.2.1 Market Drivers
2.2.2 Market Opportunities
2.2.3 Market Restraints
2.2.4 Market Challenges
2.2.5 Market Trends
2.3 Porter Five Forces Analysis
Chapter 3. Japan Rabies Vaccine Market
3.1 Japan Rabies Vaccine Market by Prophylaxis Type
3.2 Japan Rabies Vaccine Market by End User
3.3 Japan Rabies Vaccine Market by Application
3.4 Japan Rabies Vaccine Market by Product Type
Chapter 4. Company Profiles – Global Leaders
4.1 Cadila Pharmaceuticals Limited
4.1.1 Company Overview
4.1.2 Recent strategies and developments:
4.1.2.1 Product Launches and Product Expansions:
4.2 Bharat Biotech Ltd.
4.2.1 Company Overview
4.3 Serum Institute of India Pvt. Ltd. (Cyrus Poonawalla Group)
4.3.1 Company Overview
4.4 Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH
4.4.1 Company Overview
4.4.2 Financial Analysis
4.4.3 Regional & Segmental Analysis
4.4.4 Research & Development Expenses
4.4.5 SWOT Analysis
4.5 Elanco Animal Health, Inc.
4.5.1 Company Overview
4.5.2 Financial Analysis
4.5.3 Regional Analysis
4.5.4 Research & Development Expense
4.5.5 SWOT Analysis
4.6 Zoetis, Inc.
4.6.1 Company Overview
4.6.2 Financial Analysis
4.6.3 Regional Analysis
4.6.4 Research & Development Expense
4.6.5 SWOT Analysis
4.7 Merck & Co., Inc.
4.7.1 Company Overview
4.7.2 Financial Analysis
4.7.3 Segmental and Regional Analysis
4.7.4 Research & Development Expenses
4.7.5 SWOT Analysis
4.8 Novartis AG
4.8.1 Company Overview
4.8.2 Financial Analysis
4.8.3 Segmental and Regional Analysis
4.8.4 Research & Development Expense
4.8.5 SWOT Analysis
4.9 Sanofi S.A.
4.9.1 Company Overview
4.9.2 Financial Analysis
4.9.3 Segmental and Regional Analysis
4.9.4 Research & Development Expense
4.9.5 SWOT Analysis
4.10. Virbac
4.10.1 Company Overview
4.10.2 Financial Analysis
4.10.3 Regional Analysis
4.10.4 SWOT Analysis
TABLE 2 Japan Rabies Vaccine Market, 2023 - 2030, USD Million
TABLE 3 Japan Rabies Vaccine Market by Prophylaxis Type, 2019 - 2022, USD Million
TABLE 4 Japan Rabies Vaccine Market by Prophylaxis Type, 2023 - 2030, USD Million
TABLE 5 Japan Rabies Vaccine Market by End User, 2019 - 2022, USD Million
TABLE 6 Japan Rabies Vaccine Market by End User, 2023 - 2030, USD Million
TABLE 7 Japan Rabies Vaccine Market by Application, 2019 - 2022, USD Million
TABLE 8 Japan Rabies Vaccine Market by Application, 2023 - 2030, USD Million
TABLE 9 Japan Rabies Vaccine Market by Product Type, 2019 - 2022, USD Million
TABLE 10 Japan Rabies Vaccine Market by Product Type, 2023 - 2030, USD Million
TABLE 11 Key Information – Cadila Pharmaceuticals Limited
TABLE 12 Key Information – Bharat Biotech Ltd.
TABLE 13 Key Information – Serum Institute of India Pvt. Ltd.
TABLE 14 Key Information – Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH
TABLE 15 Key information – Elanco Animal Health, Inc.
TABLE 16 Key Information – Zoetis, Inc.
TABLE 17 Key Information - Merck & Co., Inc.
TABLE 18 Key Information – Novartis AG
TABLE 19 Key Information – Sanofi S.A.
TABLE 20 Key Information – Virbac
List of Figures
FIG 1 Methodology for the research
FIG 2 Japan Rabies Vaccine Market, 2019 - 2030, USD Million
FIG 3 Key Factors Impacting Rabies Vaccine Market
FIG 4 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis – Rabies Vaccine Market
FIG 5 Japan Rabies Vaccine Market share by Prophylaxis Type, 2022
FIG 6 Japan Rabies Vaccine Market share by Prophylaxis Type, 2030
FIG 7 Japan Rabies Vaccine Market by Prophylaxis Type, 2022 - 2030, USD Million
FIG 8 Japan Rabies Vaccine Market share by End User, 2022
FIG 9 Japan Rabies Vaccine Market share by End User, 2030
FIG 10 Japan Rabies Vaccine Market by End User, 2022 - 2030, USD Million
FIG 11 Japan Rabies Vaccine Market share by Application, 2022
FIG 12 Japan Rabies Vaccine Market share by Application, 2030
FIG 13 Japan Rabies Vaccine Market by Application, 2022 - 2030, USD Million
FIG 14 Japan Rabies Vaccine Market share by Product Type, 2022
FIG 15 Japan Rabies Vaccine Market share by Product Type, 2030
FIG 16 Japan Rabies Vaccine Market by Product Type, 2022 - 2030, USD Million
FIG 17 SWOT Analysis: Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH
FIG 18 SWOT Analysis: Elanco Animal Health, Inc.
FIG 19 Swot Analysis: ZOETIS, INC.
FIG 20 SWOT Analysis: Merck & Co., Inc.
FIG 21 SWOT Analysis: Novartis AG
FIG 22 Swot Analysis: Sanofi S.A.
FIG 23 SWOT Analysis: Virbac