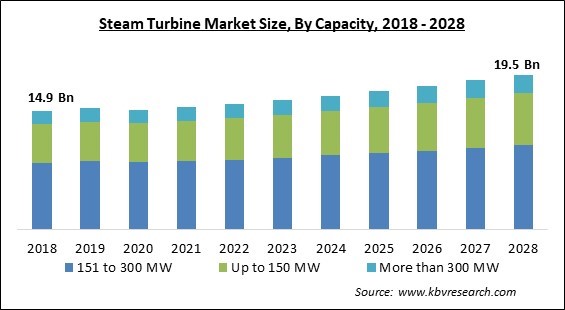
The Global Steam Turbine Market size is expected to reach $19.5 billion by 2028, rising at a market growth of 3.5% CAGR during the forecast period.
A steam turbine is a device that uses pressurized steam's thermal energy to drive mechanical work on a revolving output shaft. Modern steam turbines are made utilizing sophisticated metalworking techniques that were first made possible in the 20th century. The continuing improvement of steam turbines' resilience and efficacy are still essential to the economics and finance of the 21st century.
The utilization of many stages in the expansion of the steam, which leads to an early version of the possible response expansion process, is a major contributor to the steam turbine's gain in thermodynamic efficiency. Because the turbine produces rotating motion, it is particularly well adapted to be utilized to drive an electrical generator.
The Arabelle, a steam turbine made by GE based on an original design by Alstom, is one of the biggest steam turbines in the world as of 2021. A 7 m-diameter, 4000-ton Arabelle turbine spins at 1500 rpm and has a weight of 4000 tons. Another 4000 tons of supporting steel structure and 1000 tons of pumps, valves, and pipes are needed for a typical nuclear plant. Rotor imbalance, bearing wear, and unequal expansion are some of the technical issues (various forms of thermal shock). When operated out of trim in big installations, even the most durable rotor is capable of shattering itself.
There are two fundamental types of turbine blades: nozzles and blades. The only reason the blades move is when steam interacts with them; they do not converge in their profiles. As a result, there is a decrease in steam velocity and almost no pressure loss as steam passes through the blades. Impulse turbines, Curtis turbines, Rateau turbines, or Brown-Curtis turbines are all types of turbines that consist of blades that alternate with fixed nozzles.
The COVID-19 pandemic has slowed the expansion of the steam turbine business due to the lack of steam turbine parts, which delays their creation and creates logistical problems. Additionally, this causes ongoing projects to construct steam turbines to be delayed. Due to the steam turbine buyers' use of finances to support the COVID-19 issue, there has been a decrease in new orders for turbine installations. Manufacturers of steam turbines have since acted to supply turbines to customers with active projects. Vendors are choosing digital tools, adhering to social distance rules, and installing new power plants while donning PPE.
Due to the rapid deployment of large-scale power-generating stations, including thermal and combined cycle plants, the >3 MW - 100 MW rated steam turbines will project significant momentum. Some of the key elements promoting product adoption include the expanding use of super and ultra-super-critical technology as well as the conversion of existing power plants into combined-cycle systems. The sector dynamics will be further energized by ongoing government efforts to implement a sustainable energy network and energy-efficient technologies. The growing requirements for onsite power generation would surge the growth of the steam turbine market.
ISO works extensively with the International Electrotechnical Commission on all issues relating to electrotechnical advancements (IEC). To increase the production of mechanical steam turbines and gas extension turbines, the ISO worked with all associated organizations throughout the analysis of the steam turbine market to increase market size, share, and growth. While combined cycle plants, the most efficient kind of natural gas-fired plant, do not directly use steam turbines, natural gas plants do. In combined cycle power plants, smaller megawatt turbines are employed. The rising use of combined-cycle natural gas plants as dependable energy sources is one of the primary causes of the increase in demand for steam turbines.
Significant capital expenditures are necessary for the installation of steam turbines. Before building turbines, market participants in many locations must finish several administrative procedures and tasks, which also call for a large cost. The large costs also cover the foundation, control systems, grid connection, land, electric installation, road construction, and other expenses in addition to the installation of the turbine. The cost of installation varies from one region and one technology to another. Because of this, the market for steam turbines will face significant obstacles to expansion throughout the forecast period due to the high installation costs. The high cost of the steam turbines hinders the growth of the market.
Based on the Design, the Steam Turbine Market is segmented into Reaction and Impulse. The impulse segment acquired the highest revenue share in the steam turbine market in 2021. In this turbine, high-velocity jets of steam or water smash with the turbine's blades to rotate the turbine and generate energy. The chemical and power industries make extensive use of impulse turbines. Impulse turbines are used in the chemical industry to turn the heat energy found in hot vapors and gases into mechanical work.
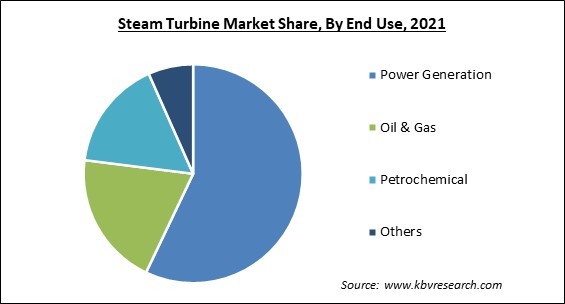
On the basis of End-use, the Steam Turbine Market is divided into Others, Power Generation, Petrochemical, and Oil & Gas. The power generation segment procured the largest revenue share in the steam turbine market in 2021. Electrical power generation applications have typically used steam turbines. The market has been divided into power and utility and industrial segments based on end-use. Any combustion fuel can be used with steam turbine units, but historically coal has been the fuel of choice. The use of coal-fired power plants and renewable energy sources like natural gas has been curtailed due to growing environmental concerns.
By Capacity, the Steam Turbine Market is classified into 151 to 300 MW, Up to 150 MW, and More than 300 MW. The more than 300 MW segment registered a significant revenue share in the steam turbine market in 2021. It is because these are utilized in nuclear and combined cycle power plants as well as steam power plants. With over 8,000 steam turbines in operation across the world, it provides proven technology suited to local circumstances.
On the basis of Technology, the Steam Turbine Market is bifurcated into Steam Cycle, Combined Cycle, and Cogeneration. The Cogeneration segment witnessed a substantial revenue share in the steam turbine market in 2021. Steam cogeneration is a high-temperature HVAC system that needs significant demand and utilization to be feasible. Cogeneration using steam turbines is only suitable for locations with power needs exceeding 1 megawatt. A steam-generated power station is a type of plant where heated water transforms into steam and drives an electricity generator via a steam turbine.
| Report Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Market size value in 2021 | USD 15.4 Billion |
| Market size forecast in 2028 | USD 19.5 Billion |
| Base Year | 2021 |
| Historical Period | 2018 to 2020 |
| Forecast Period | 2022 to 2028 |
| Revenue Growth Rate | CAGR of 3.5% from 2022 to 2028 |
| Number of Pages | 243 |
| Number of Tables | 440 |
| Report coverage | Market Trends, Revenue Estimation and Forecast, Segmentation Analysis, Regional and Country Breakdown, Companies Strategic Developments, Company Profiling |
| Segments covered | Capacity, Technology, Design, End Use, Region |
| Country scope | US, Canada, Mexico, Germany, UK, France, Russia, Spain, Italy, China, Japan, India, South Korea, Singapore, Malaysia, Brazil, Argentina, UAE, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Nigeria |
| Growth Drivers |
|
| Restraints |
|
Region-wise, the Steam Turbine Market is analyzed across North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, and LAMEA. The Asia Pacific segment procured the highest revenue share in the steam turbine market in 2021. It is because several fossil and biomass power plants are being built in nations like Indonesia, South Korea, Bangladesh, Thailand, and Japan, which will support the market's expansion throughout the forecast period, the Asia Pacific region is anticipated to keep its lead in terms of both volume and value. Because of the expanding population and quick industrialization, the region is experiencing an increase in its demand for power.
Free Valuable Insights: Global Steam Turbine Market size to reach USD 19.5 Billion by 2028
The market research report covers the analysis of key stake holders of the market. Key companies profiled in the report include General Electric (GE) Co., Siemens AG, Toshiba Corporation, Elliott Group (Ebara Corporation), Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Ltd. (Mitsubishi Power, Ltd.), MAN Energy Solutions SE (Volkswagen Group), Fuji Electric Co., Ltd., Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd., Chola Turbo Machinery International Pvt. Ltd., and Turbine Generator Maintenance, Inc.
By Capacity
By End User
By Technology
By Design
By Geography
The global Steam Turbine Market size is expected to reach $19.5 billion by 2028.
The Need For Onsite Power Generation Is Growing are driving the market in coming years, however, Costly Installation Of The Steam Turbine System restraints the growth of the market.
General Electric (GE) Co., Siemens AG, Toshiba Corporation, Elliott Group (Ebara Corporation), Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Ltd. (Mitsubishi Power, Ltd.), MAN Energy Solutions SE (Volkswagen Group), Fuji Electric Co., Ltd., Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd., Chola Turbo Machinery International Pvt. Ltd., and Turbine Generator Maintenance, Inc.
The expected CAGR of the Steam Turbine Market is 3.5% from 2022 to 2028.
The 151 to 300 MW market is generating high revenue in the Global Steam Turbine Market by Capacity in 2021, thereby, achieving a market value of $10.7 billion by 2028.
The Asia Pacific market dominated the Global Steam Turbine Market by Region in 2021, and would continue to be a dominant market till 2028; thereby, achieving a market value of $11.4 Billion by 2028.
Our team of dedicated experts can provide you with attractive expansion opportunities for your business.

