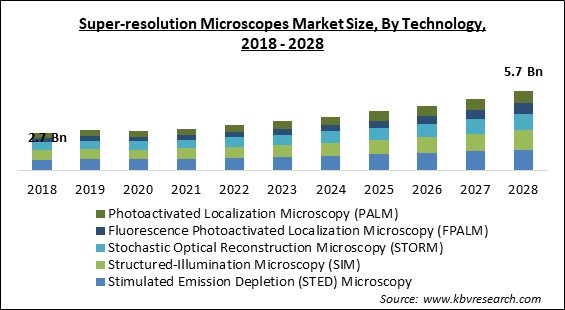
The Global Super-resolution Microscopes Market size is expected to reach $5.7 billion by 2028, rising at a market growth of 9.9% CAGR during the forecast period.
A super-resolution microscope is a form of light microscope that captures an object's picture at a higher resolution than the diffraction limit allows. There are two types of super-resolution microscopes viz. stochastically super-resolution and deterministic super-resolution. Researchers can also use these microscopes to get a close look at bacteria like the malaria virus, HIV, and other tiny microbes, which help them understand how microbes affect the human immune system. Super-resolution microscopes offer unrivaled detail and insight into the molecular world. Various companies all over the world are manufacturing a variety of super-resolution solutions for high-speed imaging applications as well as single-molecule imaging needs.
Ultrafast imaging rates enable super-resolution features in 3D samples as well as live-cell experiments to be revealed quickly with super-resolution microscopes. Super-resolution microscopes allow scientists and researchers to conduct time-lapse investigations with longer cell viability. Even with dense materials, super-resolution microscopes provide crisp super-resolution microscope images with minimal blurring. OSR methods function in real-time in order to eliminate delays caused by frame averaging and image reconstruction, resulting in instant super-resolution images and speedier results. It enables super-resolution investigations to incorporate live-cell tests, which are further enhanced by the ultrafast imaging speeds as well as multichannel acquisition capabilities of confocal.
Researchers can investigate subcellular dynamics and structures in greater detail with super-resolution light microscopy. While lightening technology doubles the spatial resolution of confocal image capture, STED technology can give nanoscale insights. Moreover, super-resolution technologies also help researchers in virology, immunology, neurology, and cancer research make breakthroughs. The diffraction limit, a physical barrier that limits optical resolution to about 250 nm and was formerly assumed to be impenetrable, is bypassed by super-resolution microscopy (SRM).
Due to the sudden shutdown of activities to prevent the spread of infection, there has been a drop in the manufacturing and supply of all types of medical devices, especially super-resolution microscopes, during the pandemic. However, the COVID-19 outbreak has propelled scientific innovation, resulting in the emergence of a wide range of applications for super-resolution microscopes since 2020. In addition, with the relaxation of production and supply constraints following COVID-19, the demand for super-resolution microscopes is likely to increase. The application of super-resolution microscopes to vital healthcare research on diseases, such as cancer is anticipated to develop, with high-order chromatin folding in preclinical carcinogenesis being revealed. The most modern microscopes, which are based on new technologies developed during the pandemic, are estimated to be in high demand.
Super-resolution microscope is clearer than various other technologies across the market. By removing background fluorescence, axial spatial resolution and contrast can be significantly improved. In addition, eliminating background disruptions can also substantially aid in the signal-to-noise (SNR) ratio. Total internal reflectance fluorescence (TIRF), as well as related evanescent wave techniques, can improve resolution if features of concern are found within 100 nm of the tissue culture or coverslip container. These techniques benefit from a phenomenon that happens when light approaching a system at an incident angle reflects at the junction between the sample medium and the coverslip.
Exploring the inner workings of cells and learning about the complexities of animal and plant growth provides the essential knowledge necessary for disease modeling and the creation of future therapeutic resources. SML microscopy's biological imaging can be utilized to track specific biomolecules or monitor biological processes. The SML microscope can view single fluorophores at significantly high speed and in three dimensions because samples are marked with chemical dyes, proteins, or quantum dots. Any scientist wishing to record real-time biological motion, which is challenging with many other microscopes will find this procedure to be of great benefit.
In the super-resolution technique known as stimulated emission depletion (STED) microscopy, two laser beams are sequentially used to stimulate and then cancel out the light. The sample is activated by the first powerful laser, which promotes fluorescence emission. All fluorescence saves that happening in a small, sub-resolution volume of the specimen is drained by the second laser, which is administered in the shape of a circle at the original site of excitation. The device scans the sample, gathering picture data from the exciting fluorochromes at each spot scanned one at a time. Although, various researchers find STED to be impracticable due to its difficult optical alignment issues. The excitation required to make an image can also be harmful to samples because STED only photographs a small portion of the fluorochromes it excites.
Based on Technology, the market is segmented into Stimulated Emission Depletion (STED) Microscopy, Structured-Illumination Microscopy (SIM), Stochastic Optical Reconstruction Microscopy (STORM), Fluorescence Photoactivated Localization Microscopy (FPALM), and Photoactivated Localization Microscopy (PALM). In 2021, the STORM technology segment garnered a significant revenue share of the super-resolution microscope market. This can be ascribed to technology breakthroughs, collaborations between different market players, and government-funded research. AX/AR confocal microscopes can be employed in conjunction with STROM microscopes. In May 2021, Nikon Corporation released the AX and AX R confocal microscopes.
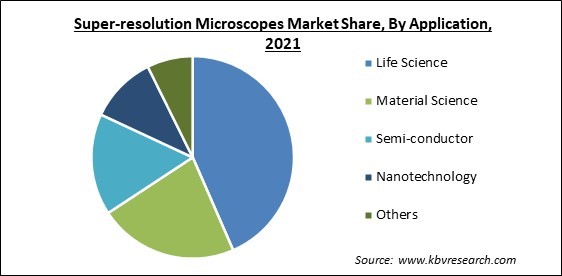
Based on Application, the market is segmented into Life Science, Material Science, Semi-conductor, Nanotechnology, and Others. In 2021, the life science segment procured the highest revenue share of the super-resolution microscope market. The rising growth of the segment is attributed to the growing use of super-resolution microscopy in research and development as well as diagnostics. Fluorescence imaging techniques with specialized probes, for example, have yielded insights into the cellular architecture of neurons in the field of neuroscience.
| Report Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Market size value in 2021 | USD 3 Billion |
| Market size forecast in 2028 | USD 5.7 Billion |
| Base Year | 2021 |
| Historical Period | 2018 to 2020 |
| Forecast Period | 2022 to 2028 |
| Revenue Growth Rate | CAGR of 9.9% from 2022 to 2028 |
| Number of Pages | 213 |
| Number of Tables | 299 |
| Report coverage | Market Trends, Revenue Estimation and Forecast, Segmentation Analysis, Regional and Country Breakdown, Competitive Landscape, Companies Strategic Developments, Company Profiling |
| Segments covered | Technology, Application, Region |
| Country scope | US, Canada, Mexico, Germany, UK, France, Russia, Spain, Italy, China, Japan, India, South Korea, Singapore, Malaysia, Brazil, Argentina, UAE, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Nigeria |
| Growth Drivers |
|
| Restraints |
|
Based on Regions, the market is segmented into North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, and Latin America, Middle East & Africa. In 2021, North America accounted for the highest revenue share of the super-resolution microscope market. The regional market is growing due to advanced healthcare facilities, substantial expenditure on R&D to better understand the mechanisms of various diseases and considerable drug development efforts in the region. In the region, extensive medical research is conducted to investigate numerous diseases' causes and pathways that are outside the scope of traditional microscopy.
Free Valuable Insights: Global Super-resolution Microscopes Market size to reach USD 5.7 Billion by 2028
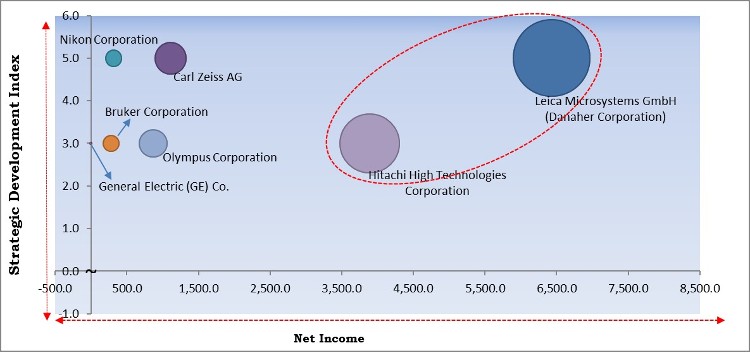
The major strategies followed by the market participants are Product Launches. Based on the Analysis presented in the Cardinal matrix; Leica Microsystems GmbH (Danaher Corporation) and Hitachi High Technologies Corporation are the forerunners in the Super-resolution Microscopes Market. Companies such as Carl Zeiss AG, Nikon Corporation, Bruker Corporation are some of the key innovators in the Market.
The market research report covers the analysis of key stake holders of the market. Key companies profiled in the report include General Electric (GE) Co. (GE Healthcare), Carl Zeiss AG, Nikon Corporation, Olympus Corporation, Leica Microsystems GmbH (Danaher Corporation), Bruker Corporation, and Hitachi High Technologies Corporation (Hitachi, Ltd.)
By Technology
By Application
By Geography
The global super-resolution microscopes market size is expected to reach $5.7 billion by 2028.
Increased clarity and precision are driving the market in coming years, however, Lack of flexibility limited the growth of the market.
General Electric (GE) Co. (GE Healthcare), Carl Zeiss AG, Nikon Corporation, Olympus Corporation, Leica Microsystems GmbH (Danaher Corporation), Bruker Corporation, and Hitachi High Technologies Corporation (Hitachi, Ltd.)
The expected CAGR of the super-resolution microscopes market is 9.9% from 2022 to 2028.
The Stimulated Emission Depletion (STED) Microscopy segment acquired maximum revenue share in the Global Super-resolution Microscopes Market by Technology in 2021, thereby, achieving a market value of $1.48 billion by 2028.
The North America market dominated the Global Super-resolution Microscopes Market by Region in 2021, and would continue to be a dominant market till 2028; thereby, achieving a market value of $1.94 billion by 2028.
Our team of dedicated experts can provide you with attractive expansion opportunities for your business.

