US Cyber Security For Industrial Automation Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report By Type, By Security Type (SCADA Security, Enterprise Security, Network Security, Device Security and Physical Security), By End Use, By Technologies, and Forecast, 2023 - 2030
Published Date : 15-Jul-2024 |
Pages: 108 |
Formats: PDF |
COVID-19 Impact on the US Cyber Security for Industrial Automation Market
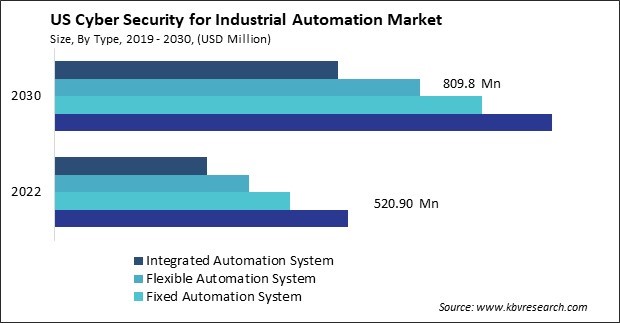
The US Cyber Security for Industrial Automation Market size is expected to reach $3.5 billion by 2030, rising at a market growth of 7.7% CAGR during the forecast period.
The cyber security for industrial automation market in the United States has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing integration of digital technologies into industrial processes and the growing awareness of cyber threats. With the proliferation of interconnected devices and systems forming the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), the attack surface for cyber threats has expanded, leaving industrial facilities vulnerable to potential breaches and disruptions.
Furthermore, the adoption of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) is playing a crucial role in enhancing the capabilities of cyber security solutions, enabling proactive threat hunting, anomaly detection, and adaptive response mechanisms. Additionally, regulatory mandates and industry standards, such as the North American Electric Reliability Corporation Critical Infrastructure Protection (NERC CIP) standards, drive organizations to implement comprehensive cyber security frameworks to ensure compliance and mitigate regulatory risks.
The U.S. cyber security for industrial automation market is characterized by diverse offerings, including threat detection and prevention systems, network security solutions, encryption technologies, and secure remote access tools. These solutions are designed to detect, defend against, and respond to cyber-attacks targeting industrial control systems (ICS), supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems, and other operational technology (OT) assets.
However, the COVID-19 pandemic has profoundly impacted the cyber security for industrial automation market in the U.S. The pandemic has accelerated the digital transformation initiatives of many organizations, leading to an expanded attack surface as remote work arrangements and increased reliance on digital technologies become the new norm. This rapid shift has heightened the urgency for robust cyber security measures to protect remote access to industrial networks and prevent potential cyber threats from disrupting critical operations.
Market Trends
Rise In Cyber Threats In The U.S.
The landscape of cyber security for industrial automation market in the United States has seen a discernible escalation in cyber threats over recent years. Phishing schemes represent significant cyber security for industrial automation market in the United States. According to the FBI's Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3), in 2022, the increasing number of cyber incidents was primarily driven by phishing schemes, which alone accounted for 300,497 of the complaints. This highlights the growing challenge in safeguarding industrial automation systems against sophisticated cyber-attacks. The adoption of the Internet of Things (IoT) devices in industrial environments has surged, enhancing efficiency and introducing vulnerabilities due to inadequate security measures in some IoT devices in the U.S.
In response to these evolving threats, the U.S. government has taken steps to bolster the cybersecurity posture of industrial automation systems. Regulatory frameworks, such as the NIST Cybersecurity Framework and the Critical Infrastructure Protection (CIP) standards enforced by the Department of Homeland Security (DHS), aim to enhance the resilience of critical infrastructure against cyber threats. Additionally, initiatives like the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) provide guidance and support to organizations in fortifying their cyber defenses.
Moreover, the emergence of ransomware as a prevalent threat vector poses grave concerns for cyber security for industrial automation market in the U.S. Ransomware attacks, such as those targeting Colonial Pipeline in 2021, underscore the vulnerability of critical infrastructure to extortion-driven cyber-attacks. The potential disruption to essential services and the economy underscores the urgent need for robust cybersecurity measures and incident response protocols. Thus, the escalating cyber threats, particularly phishing schemes and ransomware attacks, highlight the critical need for robust cybersecurity measures and regulatory frameworks to safeguard industrial automation systems in the United States.
Increasing Demand For Programmable Logic Controllers
In the United States, the demand for programmable logic controllers (PLCs) in cybersecurity for industrial automation has surged significantly in recent years. One driving factor behind the increased demand is the growing sophistication of cyberattacks targeting industrial systems. With the rise of interconnected networks and the Internet of Things (IoT), PLCs have become prime targets for malicious actors seeking to disrupt operations, steal sensitive data, or cause physical damage. This heightened risk has compelled industries across the U.S. to invest in robust cybersecurity measures, specifically securing PLCs.
Furthermore, regulatory bodies such as the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) have issued guidelines and frameworks emphasizing the importance of cybersecurity in industrial automation. This regulatory pressure has prompted organizations in the U.S. to prioritize integrating advanced security features into their PLC systems.
Moreover, the increasing adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies, such as cloud computing and big data analytics, has further fueled the demand for secure PLCs in the U.S. These technologies offer immense benefits in data analysis and operational insights. As a result, there is a growing need for PLCs equipped with robust encryption, authentication mechanisms, and intrusion detection capabilities to mitigate potential threats. Hence, the surge in demand for PLCs in the United States is driven by the escalating sophistication of cyber threats targeting industrial systems, regulatory pressure, and the adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies.
Competition Analysis
The United States is a hub for cybersecurity innovation, particularly in industrial automation. One prominent player in the U.S. cyber security for industrial automation market is Palo Alto Networks. Known for its advanced threat prevention capabilities, Palo Alto Networks offers cybersecurity products designed to protect industrial control systems (ICS) and supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems from cyber threats. Their solutions include firewall technologies, intrusion detection and prevention systems, and advanced malware protection, all integrated into a unified platform for comprehensive security management.
Cisco Systems is also a significant player in the U.S. cyber security for industrial automation market. Leveraging its expertise in networking and cybersecurity, Cisco offers a range of products and services to protect industrial networks and control systems from cyber-attacks. Their offerings include industrial firewall appliances, network visibility and monitoring tools, and security management platforms that provide real-time threat detection and response capabilities.
Another key player in the U.S. cyber security for industrial automation market is Rockwell Automation, a leading provider of industrial automation and information solutions. Rockwell Automation offers cybersecurity services specifically tailored for industrial environments, including risk assessments, security consulting, and managed security services. They also provide industrial firewalls, secure remote access solutions, and network segmentation tools to help organizations defend against cyber threats and maintain operational continuity.
In addition to these larger players, several specialized cybersecurity firms focus specifically on industrial automation security. For example, Dragos specializes in cybersecurity solutions for industrial control systems, offering threat intelligence, incident response, and asset identification services tailored for critical infrastructure sectors such as energy, manufacturing, and transportation.
Claroty is another notable player in the U.S. cyber security for industrial automation market, offering a suite of products and services for securing OT (operational technology) networks. Claroty's platform provides deep visibility into industrial networks, continuous threat monitoring, and secure remote access controls to protect against cyber-attacks and operational disruptions. As organizations continue to digitize their operations and embrace Industry 4.0 technologies, the demand for robust cybersecurity solutions tailored for industrial environments is expected to grow.
List of Key Companies Profiled
- Cisco Systems, Inc
- Schneider Electric SE
- Dell Technologies, Inc.
- Rockwell Automation, Inc.
- Honeywell International, Inc.
- IBM Corporation
- ABB Ltd.
- Microsoft Corporation
- Siemens AG
- Palo Alto Networks, Inc.
US Cyber Security for Industrial Automation Market Report Segmentation
By Type
- Programmable Automation System
- Fixed Automation System
- Flexible Automation System
- Integrated Automation System
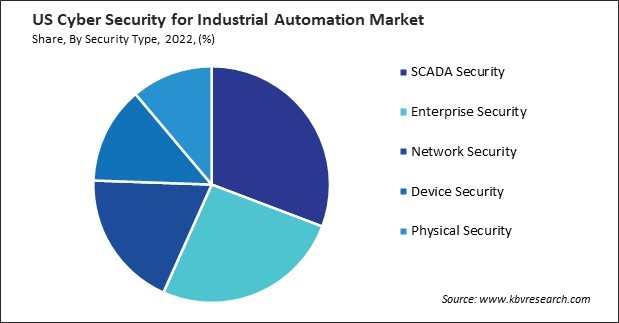
By Security Type
- SCADA Security
- Enterprise Security
- Network Security
- Device Security
- Physical Security
By End Use
- Food & Beverage Processing
- Automotive Manufacturing
- Electronics & Telecommunication
- Pharmaceuticals
- Others
By Technologies
- Programmable Logic Controllers
- Computer Numerical Control (CNC) Systems
- Industrial Sensors
- Others
1.1 Market Definition
1.2 Objectives
1.3 Market Scope
1.4 Segmentation
1.4.1 US Cyber Security for Industrial Automation Market, by Type
1.4.2 US Cyber Security for Industrial Automation Market, by Security Type
1.4.3 US Cyber Security for Industrial Automation Market, by End Use
1.4.4 US Cyber Security for Industrial Automation Market, by Technologies
1.5 Methodology for the research
Chapter 2. Market Overview
2.1 Introduction
2.1.1 Overview
2.1.1.1 Market Composition and Scenario
2.2 Key Factors Impacting the Market
2.2.1 Market Drivers
2.2.2 Market Restraints
2.2.3 Market Opportunities
2.2.4 Market Challenges
2.2.5 Market Trends
Chapter 3. Competition Analysis - Global
3.1 KBV Cardinal Matrix
3.2 Recent Industry Wide Strategic Developments
3.2.1 Partnerships, Collaborations and Agreements
3.2.2 Product Launches and Product Expansions
3.2.3 Acquisition and Mergers
3.2.4 Geographical Expansion
3.3 Market Share Analysis, 2022
3.4 Top Winning Strategies
3.4.1 Key Leading Strategies: Percentage Distribution (2019-2024)
3.4.2 Key Strategic Move: (Product Launches: 2020, Oct – 2024, Feb) Leading Players
3.5 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
Chapter 4. US Cyber Security for Industrial Automation Market
4.1 US Cyber Security for Industrial Automation Market by Type
4.2 US Cyber Security for Industrial Automation Market by Security Type
4.3 US Cyber Security for Industrial Automation Market by End Use
4.4 US Cyber Security for Industrial Automation Market by Technologies
Chapter 5. Company Profiles – Global Leaders
5.1 Cisco Systems, Inc.
5.1.1 Company Overview
5.1.2 Financial Analysis
5.1.3 Regional Analysis
5.1.4 Research & Development Expense
5.1.5 Recent strategies and developments:
5.1.5.1 Product Launches and Product Expansions:
5.1.5.2 Acquisition and Mergers:
5.1.6 SWOT Analysis
5.2 Schneider Electric SE
5.2.1 Company Overview
5.2.2 Financial Analysis
5.2.3 Segmental and Regional Analysis
5.2.4 Research & Development Expense
5.2.5 Recent strategies and developments:
5.2.5.1 Partnerships, Collaborations, and Agreements:
5.2.5.2 Product Launches and Product Expansions:
5.2.6 SWOT Analysis
5.3 Dell Technologies, Inc.
5.3.1 Company Overview
5.3.2 Financial Analysis
5.3.3 Segmental and Regional Analysis
5.3.4 Research & Development Expense
5.3.5 Recent strategies and developments:
5.3.5.1 Product Launches and Product Expansions:
5.3.6 SWOT Analysis
5.4 Rockwell Automation, Inc.
5.4.1 Company Overview
5.4.2 Financial Analysis
5.4.3 Segmental and Regional Analysis
5.4.4 Research & Development Expenses
5.4.5 Recent strategies and developments:
5.4.5.1 Partnerships, Collaborations, and Agreements:
5.4.5.2 Acquisition and Mergers:
5.4.6 SWOT Analysis
5.5 Honeywell International, Inc.
5.5.1 Company Overview
5.5.2 Financial Analysis
5.5.3 Segmental and Regional Analysis
5.5.4 Research & Development Expenses
5.5.5 Recent strategies and developments:
5.5.5.1 Partnerships, Collaborations, and Agreements:
5.5.5.2 Product Launches and Product Expansions:
5.5.5.3 Acquisition and Mergers:
5.5.6 SWOT Analysis
5.6 IBM Corporation
5.6.1 Company Overview
5.6.2 Financial Analysis
5.6.3 Regional & Segmental Analysis
5.6.4 Research & Development Expenses
5.6.5 Recent strategies and developments:
5.6.5.1 Partnerships, Collaborations, and Agreements:
5.6.5.2 Geographical Expansions:
5.6.6 SWOT Analysis
5.7 ABB Ltd.
5.7.1 Company Overview
5.7.2 Financial Analysis
5.7.3 Segmental and Regional Analysis
5.7.4 Research & Development Expense
5.7.5 Recent strategies and developments:
5.7.5.1 Product Launches and Product Expansions:
5.7.6 SWOT Analysis
5.8 Microsoft Corporation
5.8.1 Company Overview
5.8.2 Financial Analysis
5.8.3 Segmental and Regional Analysis
5.8.4 Research & Development Expenses
5.8.5 Recent strategies and developments:
5.8.5.1 Acquisition and Mergers:
5.8.6 SWOT Analysis
5.9 Siemens AG
5.9.1 Company Overview
5.9.2 Financial Analysis
5.9.3 Segmental and Regional Analysis
5.9.4 Research & Development Expense
5.9.5 Recent strategies and developments:
5.9.5.1 Product Launches and Product Expansions:
5.9.6 SWOT Analysis
5.10. Palo Alto Networks, Inc.
5.10.1 Company Overview
5.10.2 Financial Analysis
5.10.3 Regional Analysis
5.10.4 Research & Development Expense
5.10.5 Recent strategies and developments:
5.10.5.1 Product Launches and Product Expansions:
5.10.5.2 Acquisition and Mergers:
5.10.6 SWOT Analysis
TABLE 2 US Cyber Security for Industrial Automation Market, 2023 - 2030, USD Million
TABLE 3 Partnerships, Collaborations and Agreements– Cyber Security For Industrial Automation Market
TABLE 4 Product Launches And Product Expansions– Cyber Security For Industrial Automation Market
TABLE 5 Acquisition and Mergers– Cyber Security For Industrial Automation Market
TABLE 6 Geographical expansion– Cyber Security For Industrial Automation Market
TABLE 7 US Cyber Security for Industrial Automation Market by Type, 2019 - 2022, USD Million
TABLE 8 US Cyber Security for Industrial Automation Market by Type, 2023 - 2030, USD Million
TABLE 9 US Cyber Security for Industrial Automation Market by Security Type, 2019 - 2022, USD Million
TABLE 10 US Cyber Security for Industrial Automation Market by Security Type, 2023 - 2030, USD Million
TABLE 11 US Cyber Security for Industrial Automation Market by End Use, 2019 - 2022, USD Million
TABLE 12 US Cyber Security for Industrial Automation Market by End Use, 2023 - 2030, USD Million
TABLE 13 US Cyber Security for Industrial Automation Market by Technologies, 2019 - 2022, USD Million
TABLE 14 US Cyber Security for Industrial Automation Market by Technologies, 2023 - 2030, USD Million
TABLE 15 Key Information – Cisco Systems, Inc.
TABLE 16 Key Information – Schneider Electric SE
TABLE 17 Key Information – Dell Technologies, Inc.
TABLE 18 Key Information – Rockwell Automation, Inc.
TABLE 19 Key Information – Honeywell International, Inc.
TABLE 20 Key Information – IBM Corporation
TABLE 21 Key Information – ABB Ltd.
TABLE 22 Key Information – Microsoft Corporation
TABLE 23 Key Information – Siemens AG
TABLE 24 Key Information – Palo Alto Networks, Inc.
List of Figures
FIG 1 Methodology for the research
FIG 2 US Cyber Security for Industrial Automation Market, 2019 - 2030, USD Million
FIG 3 Key Factors Impacting Cyber Security for Industrial Automation Market
FIG 4 KBV Cardinal Matrix
FIG 5 Market Share Analysis, 2022
FIG 6 Key Leading Strategies: Percentage Distribution (2019-2024)
FIG 7 Key Strategic Move: (Product Launches: 2020, oct – 2024, feb) Leading Players
FIG 8 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis - Cyber Security For Industrial Automation Market
FIG 9 US Cyber Security for Industrial Automation Market share by Type, 2022
FIG 10 US Cyber Security for Industrial Automation Market share by Type, 2030
FIG 11 US Cyber Security for Industrial Automation Market by Type, 2019 - 2030, USD Million
FIG 12 US Cyber Security for Industrial Automation Market share by Security Type, 2022
FIG 13 US Cyber Security for Industrial Automation Market share by Security Type, 2030
FIG 14 US Cyber Security for Industrial Automation Market by Security Type, 2019 - 2030, USD Million
FIG 15 US Cyber Security for Industrial Automation Market share by End Use, 2022
FIG 16 US Cyber Security for Industrial Automation Market share by End Use, 2030
FIG 17 US Cyber Security for Industrial Automation Market by End Use, 2019 - 2030, USD Million
FIG 18 US Cyber Security for Industrial Automation Market share by Technologies, 2022
FIG 19 US Cyber Security for Industrial Automation Market share by Technologies, 2030
FIG 20 US Cyber Security for Industrial Automation Market by Technologies, 2019 - 2030, USD Million
FIG 21 Recent strategies and developments: Cisco Systems Inc.
FIG 22 SWOT Analysis: Cisco Systems, Inc.
FIG 23 Recent strategies and developments: Schneider Electric SE
FIG 24 SWOT Analysis: Schneider Electric SE
FIG 25 SWOT Analysis: Dell Technologies, Inc.
FIG 26 Recent strategies and developments: Rockwell Automation, Inc.
FIG 27 SWOT Analysis: Rockwell Automation, Inc.
FIG 28 Recent strategies and developments: Honeywell international, inc.
FIG 29 Swot analysis: Honeywell international, inc.
FIG 30 Recent strategies and developments: IBM Corporation
FIG 31 SWOT Analysis: IBM Corporation
FIG 32 SWOT Analysis: ABB ltd.
FIG 33 SWOT Analysis: Microsoft Corporation
FIG 34 SWOT Analysis: Siemens AG
FIG 35 Recent strategies and developments: Palo Alto Networks, Inc.
FIG 36 SWOT Analysis: PALO ALTO NETWORKS, INC.